Catalogus
Differential pressure detection is an indispensable measurement technology in industrial control systems, particularly in flow monitoring, level control, and leak detection applications. Small range pressure sensors have become the preferred solution for differential pressure detection due to their excellent measurement accuracy and stability. These sensors can provide reliable measurement data within a pressure range of 10 mbar to 7 bar, meeting the stringent requirements of various industrial applications.
1. Core Technical Features of Small Range Pressure Sensors
1.1 MEMS Technology Advantages
Small range pressure sensors are manufactured based on micro-electro-mechanical systems technology, integrating mechanical sensing elements with electronic circuits on a single chip. This technology achieves sensor miniaturization while maintaining high precision and fast response characteristics. The sensor internally uses silicon piezoresistive or capacitive sensing principles, converting minute pressure changes into measurable electrical signals. The application of MEMS technology allows sensors to significantly reduce manufacturing costs and power consumption while maintaining high performance.
1.2 Temperature Compensation Mechanism
Small range pressure sensors are equipped with advanced temperature compensation systems, achieving zero calibration and temperature drift correction through laser-trimmed thick film resistors. This design ensures stable measurement accuracy across a wide temperature range from 0 to 70°C. The temperature compensation mechanism effectively eliminates the influence of environmental temperature changes on measurement results, enabling reliable operation in harsh industrial environments.
1.3 Fast Response Performance
The 5-millisecond response time is a notable feature of small range pressure sensors, enabling them to capture rapidly changing pressure signals. In dynamic measurement applications such as pulsating flow monitoring or rapid pressure change detection, this fast response capability is particularly important. The sensor’s fast response ability combined with high precision measurement provides reliable data support for real-time control systems.
2. Technical Requirements and Challenges for Differential Pressure Detection
2.1 Measurement Accuracy Requirements
Differential pressure detection applications impose strict accuracy requirements on sensors, especially in medical devices and precision industrial control. Small range pressure sensors achieve excellent linearity throughout the measurement range through precise zero calibration and span calibration. The sensor’s nonlinearity error is controlled within the minimum range, ensuring accuracy and reliability of measurement data.
2.2 Long-term Stability Challenges
Industrial differential pressure detection typically requires long-term continuous operation, challenging sensor stability. Small range pressure sensors employ ceramic substrates and metal packaging technology, providing excellent long-term stability. The sensor’s repeatability error is controlled within a very small range, ensuring measurement accuracy consistency during long-term use.
2.3 Media Compatibility Requirements
Different application scenarios have varying requirements for sensor media compatibility. Small range pressure sensors support measurement of dry air, non-corrosive gases, and liquids, meeting the needs of most industrial applications. The sensor’s two pressure ports are optimized for different media, ensuring reliability under various working conditions.
3. Major Application Field Analysis
3.1 Medical Device Applications
In medical devices, small range pressure sensors are widely used in ventilators, blood pressure monitoring equipment, and drug delivery systems. These applications require extremely high sensor precision, response speed, and biocompatibility. The sensor’s 5-millisecond response time and high-precision measurement capability ensure medical device safety and effectiveness. In ventilator applications, sensors accurately monitor patient respiratory pressure changes, providing reliable data for medical diagnosis.
3.2 HVAC Systems
Differential pressure detection in HVAC systems is crucial for ensuring indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Small range pressure sensors can precisely measure pressure differentials across filters, promptly detecting filter blockage issues. The sensor’s wide temperature compensation range adapts to HVAC system working environments, ensuring measurement accuracy under different seasonal and temperature conditions.
3.3 Industrial Process Control
In industrial process control, differential pressure measurement is used for flow calculation, level monitoring, and leak detection. The high precision and fast response characteristics of small range pressure sensors enable them to meet real-time data requirements in industrial automation. The sensor’s constant current excitation design simplifies circuit configuration, reducing system integration complexity.
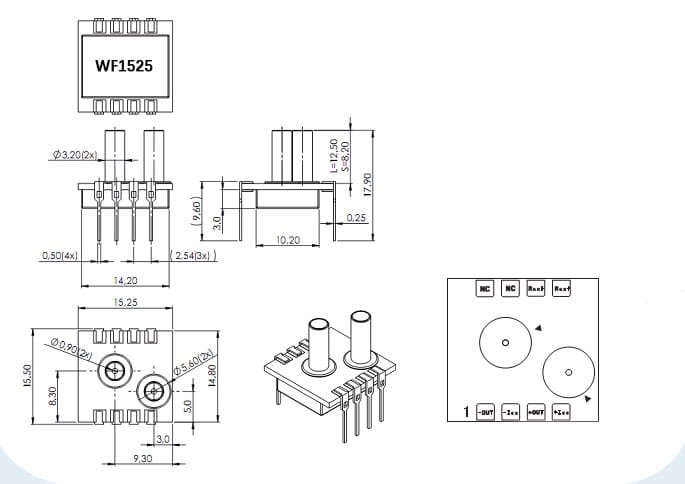
4. Selection and Integration Considerations
4.1 Range Selection Principles
Selecting an appropriate sensor range is crucial for ensuring measurement accuracy. Small range pressure sensors provide wide range options from 10 mbar to 7 bar, and engineers should choose suitable models based on actual application pressure ranges. Range selection should consider measurement accuracy requirements, overpressure protection needs, and system safety margins.
4.2 Output Signal Processing
Small range pressure sensors provide analog voltage output, with signals proportional to input current. In system integration, appropriate signal conditioning circuits and differential amplifiers need to be configured. The sensor’s output signal characteristics simplify subsequent signal processing work, reducing system design complexity.
4.3 Mechanical Installation Requirements
The sensor’s DIP package format facilitates PCB installation and system integration. In mechanical design, sensor installation direction, connection methods, and sealing requirements must be considered. The sensor’s compact design adapts to modern electronic device miniaturization trends, providing greater flexibility for system design.
5. Performance Optimization and Maintenance Strategies
5.1 Calibration and Adjustment
Small range pressure sensors undergo zero calibration and span calibration before leaving the factory, but still require periodic calibration during long-term use. The calibration process should use standard pressure sources to ensure long-term stability of measurement accuracy. Reasonable calibration cycles and standardized calibration procedures are important measures for maintaining sensor performance.
5.2 Environmental Protection Measures
The sensor’s working environment significantly impacts its performance and lifespan. When used in harsh environments, appropriate protection measures should be taken, such as dust-proof, moisture-proof, and anti-corrosion treatments. The sensor’s media compatibility limitations restrict its application in certain corrosive environments, requiring consideration during selection.
5.3 Fault Diagnosis and Prevention
Establishing comprehensive fault diagnosis mechanisms helps identify sensor problems promptly. Common failure modes include zero drift, span changes, and response time extension. By monitoring sensor output signal characteristics, potential problems can be detected early and preventive measures taken.
Conclusie
Small range pressure sensors have become the ideal choice for differential pressure detection measurement due to their excellent technical performance and wide application adaptability. MEMS technology application achieves sensor miniaturization and high performance, temperature compensation mechanisms ensure measurement accuracy stability, and fast response characteristics meet real-time control requirements. In medical devices, HVAC, and industrial process control fields, these sensors demonstrate outstanding performance. Proper selection, reasonable integration design, and standardized maintenance strategies are key factors for achieving optimal sensor performance. With continuous development of industrial automation technology, small range pressure sensors will play important roles in more fields.
De bovenstaande introductie schetst slechts het oppervlak van de toepassingen van druksensortechnologie. We zullen doorgaan met het verkennen van de verschillende soorten sensorelementen die in verschillende producten worden gebruikt, hoe ze werken en hun voor- en nadelen. Als u meer informatie wilt over wat hier wordt besproken, kunt u de gerelateerde inhoud verderop in deze handleiding bekijken. Als u weinig tijd heeft, kunt u ook hier klikken om de details van deze handleidingen te downloaden Luchtdruksensorproduct PDF -gegevens.
Voor meer informatie over andere sensortechnologieën kunt u terecht Bezoek onze sensorenpagina.

This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward
to seeking more of your great post. Also, I’ve
shared your web site in my social networks!