Датчики TPMS контролюють тиск у шинах у режимі реального часу та попереджають водія за допомогою сигнальних індикаторів. Існують прямий, непрямий і гібридний типи, причому прямий тип забезпечує точні показання, але за високу вартість, а непрямий тип коштує менше, але не вимірює тиск повітря безпосередньо. TPMS покращує безпеку, подовжує термін служби шин і покращує паливну ефективність, запобігаючи погіршенню керованості та погіршенню гальмування через недостатній тиск у шинах.
Починаємо читати!
Зміст
1. Що таке TPMS?
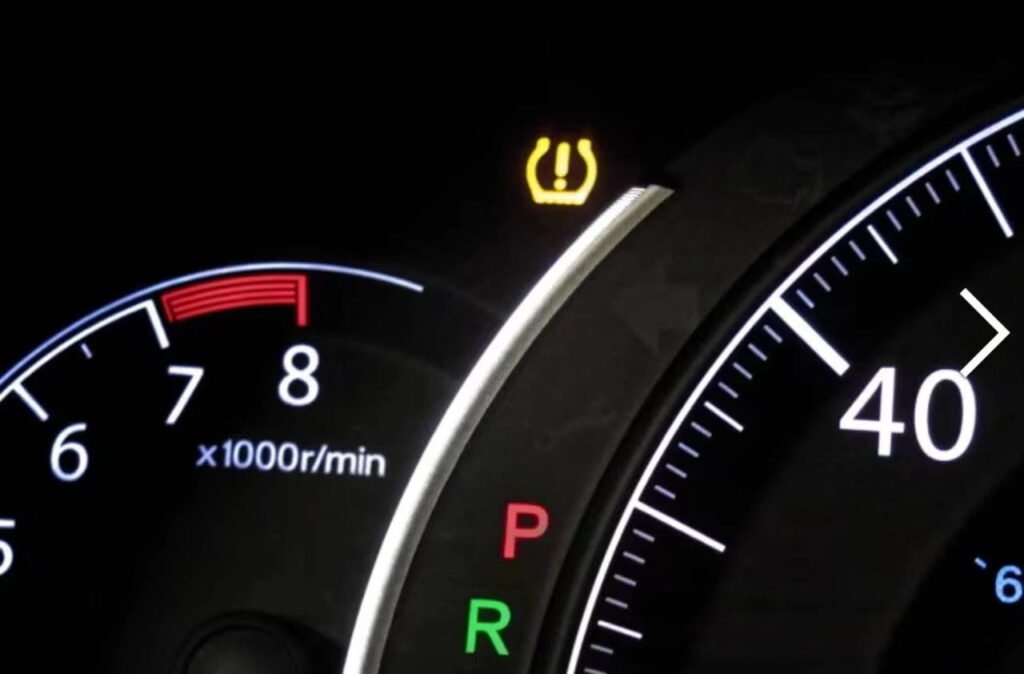
Система TPMS с Датчик тиску в шинах (TPS) забезпечує визначення тиску в шинах у режимі реального часу та сповіщення водія за допомогою попереджувальних індикаторів на панелі приладів, піктограм або манометрів. Системи TPMS вперше з’явилися в деяких розкішних і високопродуктивних транспортних засобах у 1980-х або на початку 1990-х років, перш ніж набули широкого поширення. З початку 2000-х років TPMS є обов’язковою функцією нових автомобілів. Низький тиск у шинах запускає попереджувальну лампу на панелі приладів, щоб попередити водія про потенційно небезпечну ситуацію.
Тиск у шинах дуже реально впливає на керованість автомобіля та гальмування, а також може зменшити економію палива завдяки підвищеному опору коченню. Недостатньо накачані шини збільшать споживання палива, а недостатньо накачані шини матимуть надмірну гнучкість боковини, що призведе до нестабільної та небезпечної керованості. Крім того, підвищений опір коченню та тертя можуть призвести до перегріву та швидшого зношування шин, що робить дуже ймовірним вибух на швидкості шосе. За підрахунками, приблизно одна третина всіх легкових, вантажних автомобілів, мікроавтобусів і позашляховиків на шосе використовують шини з недостатнім тиском. За підрахунками, несправність шин через недостатнє накачування призводить до 40 000 аварій, 33 000 травм і 650 смертей щорічно.

2. Типи TPMS
Наразі пропонуються три основні типи систем контролю тиску в шинах (TPMS):
Прямий TPMS:
Прямі системи використовують фактичні датчики для зв’язку з бортовим приймачем автомобіля для моніторингу тиску та температури всередині шини.
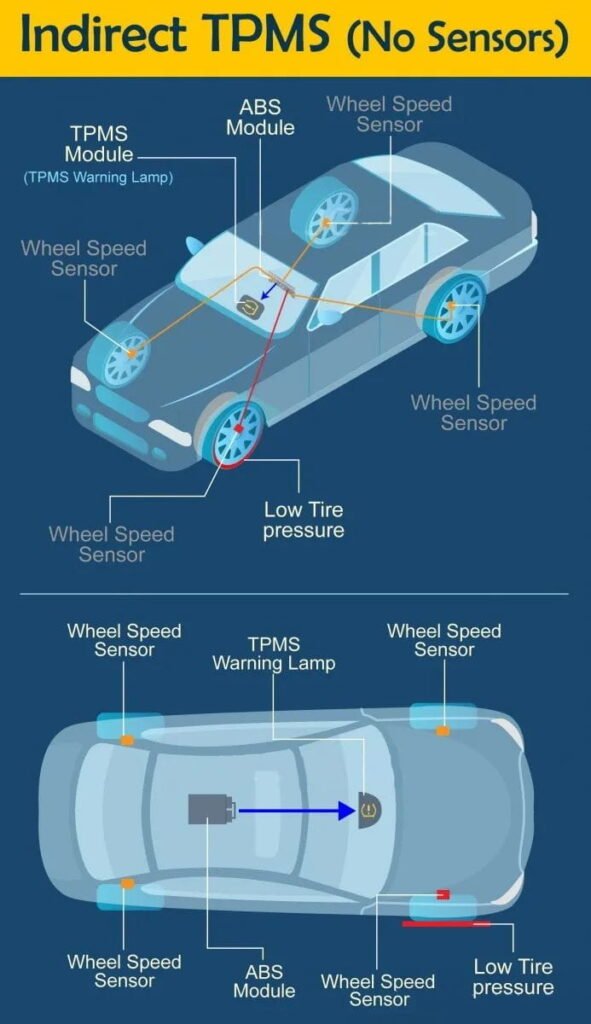
Непрямий TPMS:
Замість використання фактичного датчики тиску всередині колеса для контролю єдиного тиску, непрямі системи фактично використовують систему ABS автомобіля для вимірювання швидкості обертання кожної шини. Невелика різниця в тиску в шинах може призвести до того, що одна або кілька шин обертатимуться з іншою швидкістю, ніж інші, що виявляє система та загоряється індикатор TPMS. Несправні датчики швидкості коліс або водіння у вологих умовах також можуть спричинити загоряння індикатора TPMS у таких системах.
Гібридний TPMS:
Внутрішні датчики шини працюють у поєднанні з датчиками швидкості коліс, щоб допомогти водієві (через індикатор на панелі приладів) повідомити, яка шина недостатньо накачана.
2.1 Непрямий TPMS
Непрямий TPMS зазвичай покладається на датчики швидкості коліс, які використовуються в антиблокувальних системах гальм. Ці датчики вимірюють швидкість обертання кожного колеса, яку бортова комп’ютерна система порівнює з іншими робочими даними автомобіля, наприклад швидкістю автомобіля. На основі швидкості обертання кожного колеса комп’ютер інтерпретує відносний розмір шин автомобіля. Коли колесо починає обертатися швидше, ніж очікувалося, комп’ютер обчислює, що шина недостатньо накачана, і відповідно попереджає водія. Тому система непрямого контролю тиску в шинах насправді не вимірює тиск у шинах. Він не обробляє вимірювання електронним способом, як манометр у шинах. Натомість непрямий монітор тиску просто вимірює швидкість обертання шини та надсилає сигнал до комп’ютера, який активує індикатор, коли виникає проблема під час обертання.
Переваги непрямого TPMS
- Відносно недорогий порівняно з прямим TPMS
- Менше загального встановлення та обслуговування, ніж пряма TPMS
Недоліки непрямого TPMS
- Може бути неточним, якщо придбати більші або менші шини
- Вимірювання тиску в шинах може бути ненадійним, якщо шини зношені нерівномірно
- Потрібне скидання після накачування кожної шини
- Потрібно скинути після щоденної заміни шин
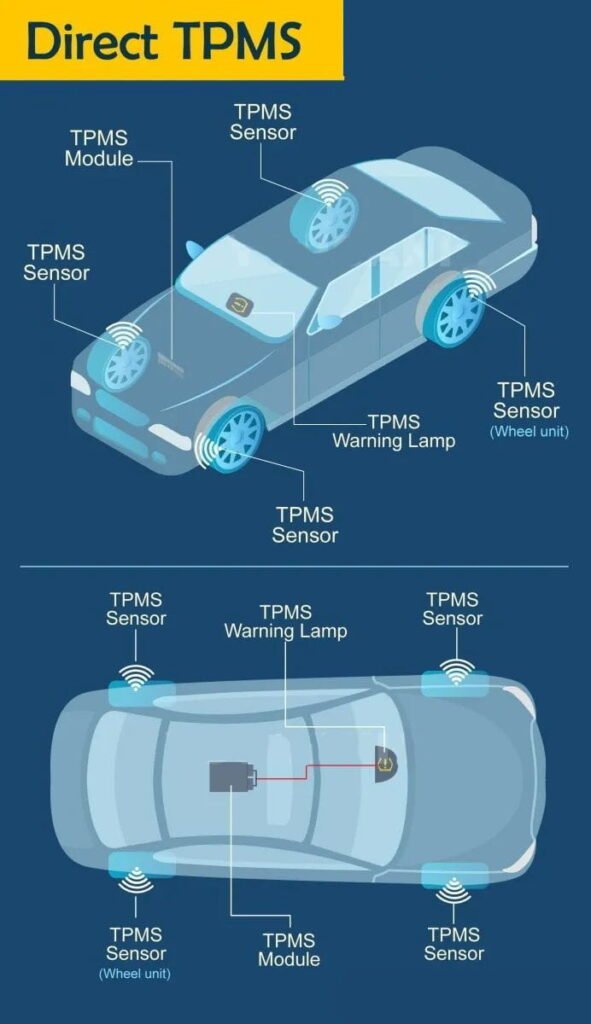
2.2 Прямий TPMS
Пряме використання TPMS датчики контролю тиску у кожній шині, щоб контролювати певні рівні тиску, а не лише дані про швидкість колеса від антиблокувальної гальмівної системи. Датчики в системі DPM також вимірюють температуру шин.
Система прямого контролю тиску в шинах надсилає всі ці дані до центрального модуля керування, де вони аналізуються та інтерпретуються, і якщо тиск у шинах нижчий, ніж повинен бути, вони передаються безпосередньо на панель приладів, де загоряється індикатор. Прямі вимірювачі тиску в шинах зазвичай надсилають усі ці дані по бездротовому зв’язку. Кожен датчик має унікальний серійний номер.
Переваги Direct TPMS
- Забезпечує фактичні показники тиску в шинах на основі внутрішніх вимірювань шин;
- Відсутність помилок через заміну шин;
- Проста повторна синхронізація після заміни шин;
- Батарейки в датчику зазвичай вистачає на 5-10 років.
Недоліки Direct TPMS
- Загальна ціна дорожча, ніж непрямий TPMS.
- Акумулятор не обслуговується; якщо батарея розряджена, необхідно замінити весь датчик.
- Датчики легко пошкодити під час монтажу/демонтажу.
3. Переваги TPMS
Основна користь від датчик TPMS полягає в тому, щоб надавати водіям важливу інформацію про тиск у шинах, повідомляючи їм, коли їхні шини недостатньо накачані, і запобігаючи виникненню небезпечних ситуацій. Неправильно накачані шини можуть вплинути на керованість, ефективність гальмування та економію палива, а також призвести до розриву шин на високих швидкостях.
Безпека
Недостатньо накачані шини мають погану керованість, погане гальмування, непередбачувані повороти та дуже нестабільні, тому важливо точно вимірювати тиск у шинах.
Знос шин
Недостатньо накачані шини зношуються по краях і плечах, оскільки їх слід на дорозі деформується вагою автомобіля, і цей знос може призвести до скорочення терміну служби протектора шини. Що ще гірше, недостатньо накачані шини виділяють більше тепла, що пошкоджує цілісність самої шини, що призводить до передчасного зносу сталевих ременів і волокон і, можливо, до розшарування протектора.
Ефективність палива
Недостатньо накачані шини збільшують опір коченню та тертя, змушуючи двигун вашого автомобіля працювати інтенсивніше, що, у свою чергу, впливає на економію палива.
Висновок
Датчики TPMS є незамінною функцією безпеки в сучасних автомобілях, допомагаючи водіям виявляти потенційні проблеми в режимі реального часу, контролюючи тиск і температуру в шинах. Незалежно від того, чи є вони прямими, непрямими чи гібридними TPMS, вони відіграють важливу роль у підвищенні безпеки водіння, подовженні терміну служби шин і покращенні паливної ефективності. Правильне технічне обслуговування та використання датчиків TPMS не тільки покращує враження від водіння, але й запобігає нещасним випадкам, спричиненим несправністю шин, забезпечуючи безпечніші умови водіння для водіїв і пасажирів.
