Have you ever wondered how a machine can interpret its environment and react accordingly? The answer lies in analog Ve digital sensors. Analog sensors enable machines to collect data from their environment, interpret it, and make decisions based on the information. For example, a car can detect obstacles in its path and a medical device can monitor vital signs. Digital sensors utilize software algorithms to interpret their inputs and generate outputs. They are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of machines.
In this article, we will look at analog and digital signals, the differences between analog and digital sensors, how they work, and the different types of applications in which they are used.
Summary:
- Signals and Their Types
- Analog ve Dijital Sensörler
- Types of Analog and Digital Sensors
- Applications of Analog and Digital Sensors
- Çözüm
Signals and their types
What is Analog Vs Digital?
Analog and digital signals are both methods of transmitting information. The significant difference between digital signals and analog signals is their electrical properties-analog signals are characterized by a continuous current, while digital signals are characterized by a non-continuous pulse.
Both analog and digital signals have their advantages and disadvantages, depending on their use. Analog signals typically have better noise immunity and greater bandwidth, but require more complex circuitry to process them, while digital signals typically have simpler circuitry, but tend to have a higher degree of distortion due to quantization errors in reducing a large number of bits to smaller ones. Therefore, when deciding which type of signal should be used for any given application, it is important to consider all aspects of the particular task at hand to find the best choice for that particular situation.
What is analog signal?
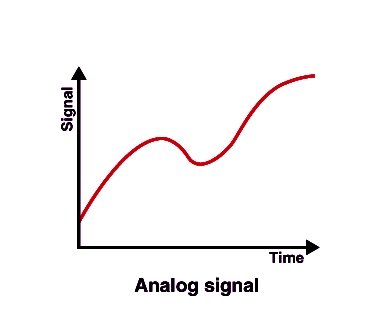
Analog signals are continuous waveforms that represent physical measurements, such as electrical currents or sound waves. They are typically generated by analog sensors such as microphones and thermocouples, and can be transmitted over a cable or wireless connection. The amplitude of an analog signal is proportional to the value of the measurement, which means it carries more information than a digital signal.
What is the Most Common Analog Signal?
The most common analog signal is electrical current, which comes from analog sensors such as thermocouples and is used to measure a variety of physical properties, including temperature, pressure, and sound level. To transmit these signals, cable or wireless connections can be used, but they can be interfered with by interfering noise, which requires special care during transmission.
What is digital signal?
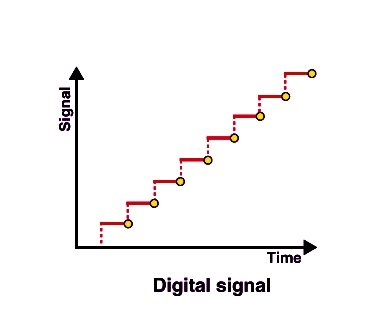
Digital signals are discontinuous and represent binary values that can only be interpreted as zero or one. This makes them easier for computers to store and process than analog signals. Digital signals use discrete pulses to represent data rather than the smooth waveforms found in analog signals. Digital signals can be transmitted over long distances without loss of information or damage from external sources. As a result, they are becoming more common in modern communication systems.
Which is better, analog or digital signals?
It depends on the use case. Analog signals can convey more information because their amplitude is proportional to the measurement being made, but digital signals are more accurate and resistant to noise. For applications where precision and accuracy are critical, digital signals may be the better choice. For applications where a larger range of information needs to be transmitted, analog signals may be more appropriate.
Analog Sensors Vs Digital Sensors
Sensors can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Analog sensors
- Digital sensors
Both types of sensors have their uses, depending on the application.
What is Analog Sensor?
Analog sensors are devices that measure physical attributes such as temperature, pressure, or sound level and output an analog signal. They range from simple devices such as thermometers to more advanced technologies such as strain gauges. Analog sensor outputs are usually analog in nature and require further processing to interpret.
What does the analog sensor read?
An analog sensor reads physical attributes such as temperature, pressure, or sound level. It usually outputs analog signals which can then be processed to interpret the measurement. Analog sensors are often used in applications that require higher accuracy and/or lower noise interference than digital sensors. For example, temperature readings from precision instruments may require analog sensors because of their ability to detect small changes in the measured parameters.
What does the analog sensor read?
Analog pressure sensors, sound sensors, temperature sensors, and light sensors (LDRs) are some examples of analog sensors.
What is the advantage of analog sensors?
The main advantage of analog sensors is the ability to measure physical phenomena of various values. For example, a thermometer can measure temperatures that vary from low to high depending on the type of sensor used. Similarly, strain gauges and photoelectric detectors can be used to measure large ranges of force or light intensity, respectively.
What is Digital Sensor?
Digital sensors are physical sensors that measure physical quantities and convert them into usable digital signals. They work by detecting changes in the environment, such as temperature, pressure, or sound waves, and converting this information into a digital format. Common digital sensors include thermistors (temperature), piezoelectric crystals (pressure), and microphones (sound). The most common type of digital sensor is an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which converts analog signals from a device or environment into digital format.
What is the digital sensor example?
Digital pressure sensors and temperature sensors are two examples of commonly used digital sensors.
Types of Analog & Digital Sensors
List of analog sensor types:
- Analog Accelerometers
- Analog Light Sensors
- Analog Sound Sensors
- Analog Basınç Sensörleri
- Analog Temperature Sensors
Analog Accelerometers: Analog accelerometers are analog sensors used to measure acceleration or vibration. These sensors convert acceleration into an observable signal. They are commonly installed on various structures such as airplanes, vehicles and bridges to track vibrations generated by movement or traffic. With their high sensitivity and fast response time, analog accelerometers can also be used inside machinery to monitor its health.
Analog Light Sensors: Analog light sensors are a type of analog sensor used to measure light intensity. They work by converting the received light into a telecommunication signal that can be monitored. Common applications for analog light sensors include measuring the amount of natural daylight in a room, controlling the illumination level of buildings and streetlights, and cameras used to measure exposure.
Analog Sound Sensors: Analog sound sensors are a type of analog sensor used to measure the intensity of sound. They work by converting the received sound into a telecommunication signal that can be monitored. Analog sound sensors are commonly used to determine noise levels in industrial environments and to evaluate the audio quality of music studios.
Analog Pressure Sensors: Analog pressure sensors are a type of analog sensor used to measure pressure. They work by converting the received pressure into a telecommunication signal that can be monitored. Pressure sensors are used for control and monitoring in thousands of everyday applications. These sensors can also indirectly measure several other variables, including fluid and gas flow, velocity, water level, and altitude. Analog pressure sensors have fast response times and good sensitivity, and are easy to calibrate.
Analog Temperature Sensors: Analog temperature sensors are analog sensors used to measure temperature. They work by converting the received temperature into a signal that can be monitored. Thermistors are common temperature sensor analogs, and there are different types depending on their specific use. Analog temperature sensors work by detecting changes in temperature because they are actually heat sensitive resistors. The resistance of a thermistor increases as the temperature increases and decreases as the temperature decreases. It is used in various temperature sensor applications.
List of Digital sensor types:
- Digital Accelerometer Sensor
- Digital Temperature Sensor
- Digital Humidity Sensor
Digital Accelerometer Sensors: Digital accelerometers are digital sensors used to measure acceleration. Their function is to convert the collected acceleration into an observable signal. Digital accelerometers are widely used in industrial environments to determine vibrations and shocks, and in robotics projects or navigation systems to record position and angle.
Digital Temperature Sensors: Digital temperature sensors are used to measure temperature and monitor it by converting the observed temperature into a telecommunication signal. Common applications for digital temperature sensors include monitoring temperature in industrial environments, controlling greenhouse environments, and measuring the overall temperature of soil, air or water in agricultural applications.
Digital Humidity Sensors: Digital humidity sensors are used to detect and measure humidity levels in the environment. Humidity sensors can be used in a variety of applications such as climate control systems, agricultural monitoring, medical equipment and industrial production.
How to determine if a sensor is analog or digital?
There are several ways to determine whether a sensor is an analog or digital sensor. A few common methods are described below:
Output Signal: One of the easiest ways to determine whether a sensor is an analog or digital sensor is to examine its output signal. Analog sensors typically output a continuous voltage or current proportional to the variable being measured, while digital sensors output a series of digits or digital codes.
Interface: Another way to determine whether a sensor is analog or digital is to look at the interface it uses to communicate with the device or system it is connected to. Analog sensors typically use an analog electrical interface, such as a voltage or current output, while digital sensors use a digital interface, such as a serial or parallel bus.
Data Sheet: The data sheet for a sensor usually specifies whether the sensor is an analog or digital sensor. This is the most reliable way to find out what type of sensor it is.
External Components: Some sensors require external components, such as an ADC (analog-to-digital converter), to convert the analog signal to a digital signal. If the sensor requires an ADC, then it is an analog sensor.
It is important to note that some sensors may have both analog and digital outputs, or both analog and digital interfaces. In this case, it is important to check the sensor’s datasheet or consult the manufacturer to determine the type of output or interface being used.
Analog and Digital Sensor Applications

The following are analog sensor applications:
In the industrial field, analog pressure sensors are widely used in the petroleum, chemical, and steel industries to monitor parameters such as hydraulic pressure, gas pressure, and liquid level to ensure the stability and safety of production processes. At the same time, it can also help enterprises to realize energy saving and productivity improvement.
In the medical field, analog pressure sensors are used in monitors, sphygmomanometers, anesthesia machines, and other medical equipment to instantly monitor the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs, providing doctors with accurate diagnostic basis. In addition, it can also help doctors realize fast and accurate surgical operations, improving the safety and success rate of surgery.
In the automotive field, simulated pressure sensors are used in automotive power systems, braking systems, safety systems, etc., to monitor parameters such as oil pressure, air pressure and temperature to ensure the safety and stability of automobile driving. At the same time, it can also help drivers to realize energy saving and emission reduction.
In the field of environmental protection, analog pressure sensors are used in atmospheric monitoring stations, water quality monitoring stations and other equipment to monitor the environment, such as air pressure, water level, temperature and other parameters, to provide scientific data support for environmental protection. At the same time, it can also help enterprises to realize the implementation of environmental protection measures and the goal of energy saving and emission reduction.
In the field of aviation, simulated pressure sensors are used in the hydraulic and pneumatic systems of aircraft to monitor parameters such as air pressure and oil pressure to ensure the safety and stability of aircraft flight. At the same time, it can also help pilots to realize energy saving and emission reduction.
In the agricultural field, analog pressure sensors are used in irrigation systems to monitor water level and pressure to ensure the normal operation of the irrigation system and the effective use of water. At the same time, it can also help farmers to realize energy saving and water utilization efficiency.
The following are digital sensor applications:
In the field of industrial automation, digital pressure sensors are widely used to measure air pressure, oil pressure, water pressure, etc., for monitoring and controlling the pressure changes in pumps, valves, pipelines, containers, tanks, and machinery and equipment. For example, in the oil pipeline, water conservancy and hydropower, railway and transportation, intelligent building and other fields, digital pressure sensors play an important role.
In the field of transportation, digital pressure sensors are used to monitor the pressure of the vehicle braking system, tire pressure, airbag system pressure, etc. to ensure the safe operation of traffic. For example, in smart cars, digital pressure sensors can monitor tire pressure in real time to ensure driving safety.
In medical equipment, digital pressure sensors are widely used in blood pressure monitors, respirators and other equipment, used to monitor the body’s internal pressure changes, such as heart and lung pressure, to help doctors diagnose and treat cardiovascular disease, respiratory system diseases.
In the field of consumer electronics, digital pressure sensors are used in devices such as smart phones, for example, to detect the pressure of keystrokes and provide a more accurate and reliable input experience.
Çözüm
Both analog and digital sensors are powerful tools for collecting environmental data. Analog sensors provide more direct and accurate measurements of physical phenomena such as temperature, pressure, and sound. Digital sensors use software algorithms to interpret their inputs, making them suitable for more complex applications.
Each type of sensor has its own advantages and limitations that must be considered when selecting a sensor for a particular application. Understanding how analog and digital sensors work is essential for any application involving environmental monitoring.
What else would you like to know? Or have some questions?
Either way, please comment below or contact us.


