Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) pressure sensors are widely used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace and medical, and have become important devices for modern engineering by virtue of their high accuracy and small size. In recent years, pressure sensors have made significant advances in design, manufacturing and packaging technologies, and their performance has been significantly improved. In this paper, we will discuss the latest trends in micro differential pressure sensors (MDPS), resonant pressure sensors (RPS), integrated sensing chips, and miniaturized pressure sensors.

Каталог
Да почнеме да разбираме!
1.Basic Principles of MEMS Pressure Sensors
MEMS pressure sensors operate based on piezoresistive, capacitive, piezoelectric or resonant principles. For example, piezoresistive sensors measure pressure through a Wheatstone bridge and have high sensitivity. However, factors such as high temperature drift affect their accuracy, which has become a challenge limiting their development. Capacitive sensors are characterized by low power consumption and good temperature stability, but parasitic effects have an impact on their accuracy.
2. Micro Differential Pressure Sensor (MDPS)
MDPS is widely used in medical equipment, fire outlet pressure monitoring, etc. It is especially suitable for high-precision measurements in small pressure ranges. In recent years, MDPS has evolved from the traditional flat membrane structure to a more complex “beam-membrane-island” design to improve sensitivity and reduce non-linearity.
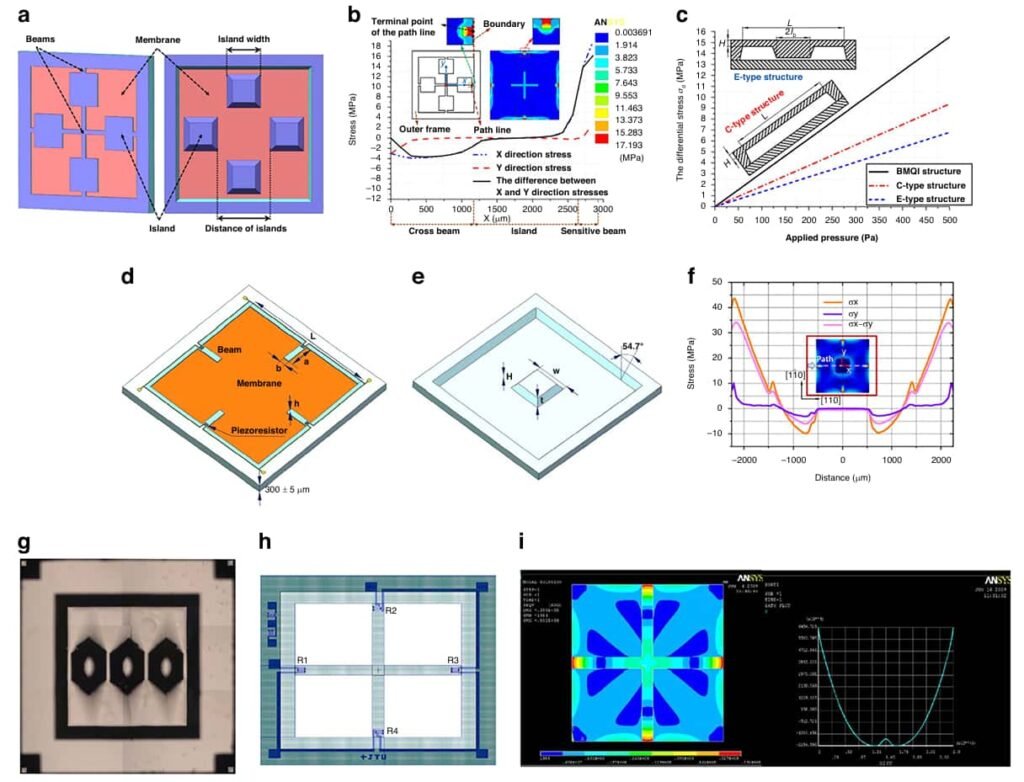
Figure 1 illustrates the evolution of the MDPS design from a flat membrane to a beam-membrane island, with a significant increase in sensitivity and a more optimized stress concentration.
This structure achieves a sensitivity of 11.098 μV/V/Pa in the range of 0-500 Pa, which is a significant improvement over the C-type and flat membrane structures. Subsequent optimizations include a cross beam design and a hollow island structure to further improve the stress distribution and dynamic performance.
3. MDPS Manufacturing Technology
MDPS fabrication requires high-precision etching processes, including deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) and boron doping processes, for forming the piezoresistors. Etching the stop layer is critical to control the thickness of the diaphragm and helps maintain high sensitivity.
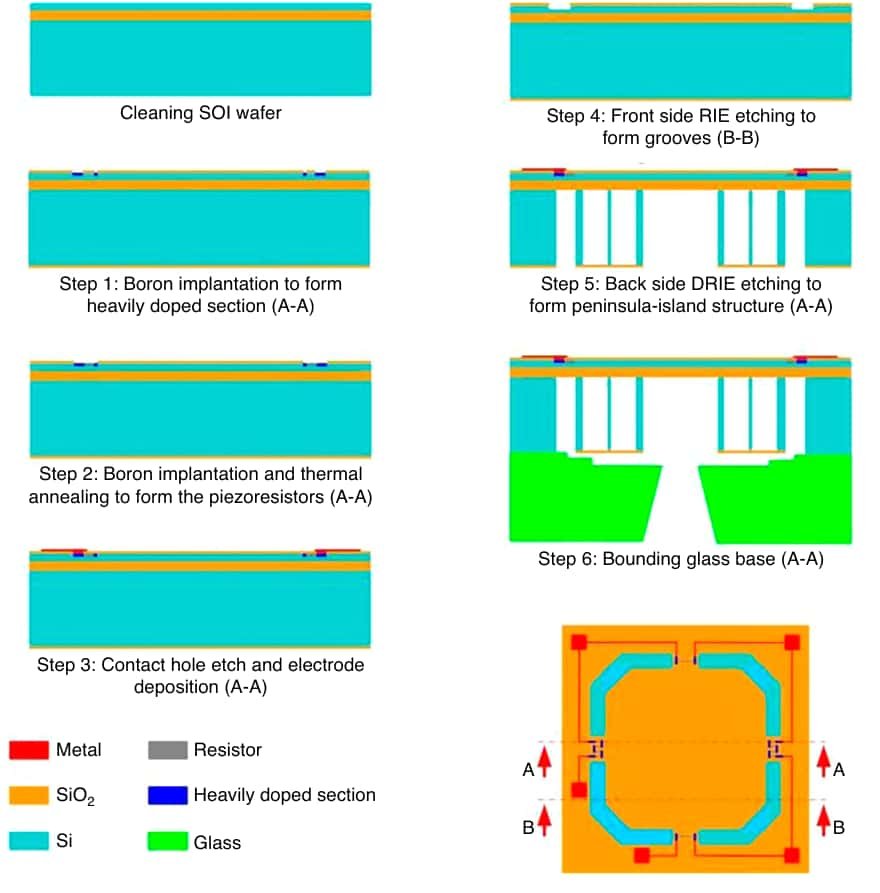
- Figure 2 illustrates the key steps in the fabrication of MDPS, emphasizing the importance of etching accuracy for film uniformity.
- The integration of signal amplification circuitry further enhances sensitivity, with some designs achieving 44.9 mV/V/kPa.
4.Resonant Pressure Sensors (RPS)
Resonant pressure sensors are widely used in high-end fields such as aerospace and weather monitoring due to their high accuracy and stability. These sensors realize pressure measurement by measuring the characteristics of resonant beam frequency variation with pressure.
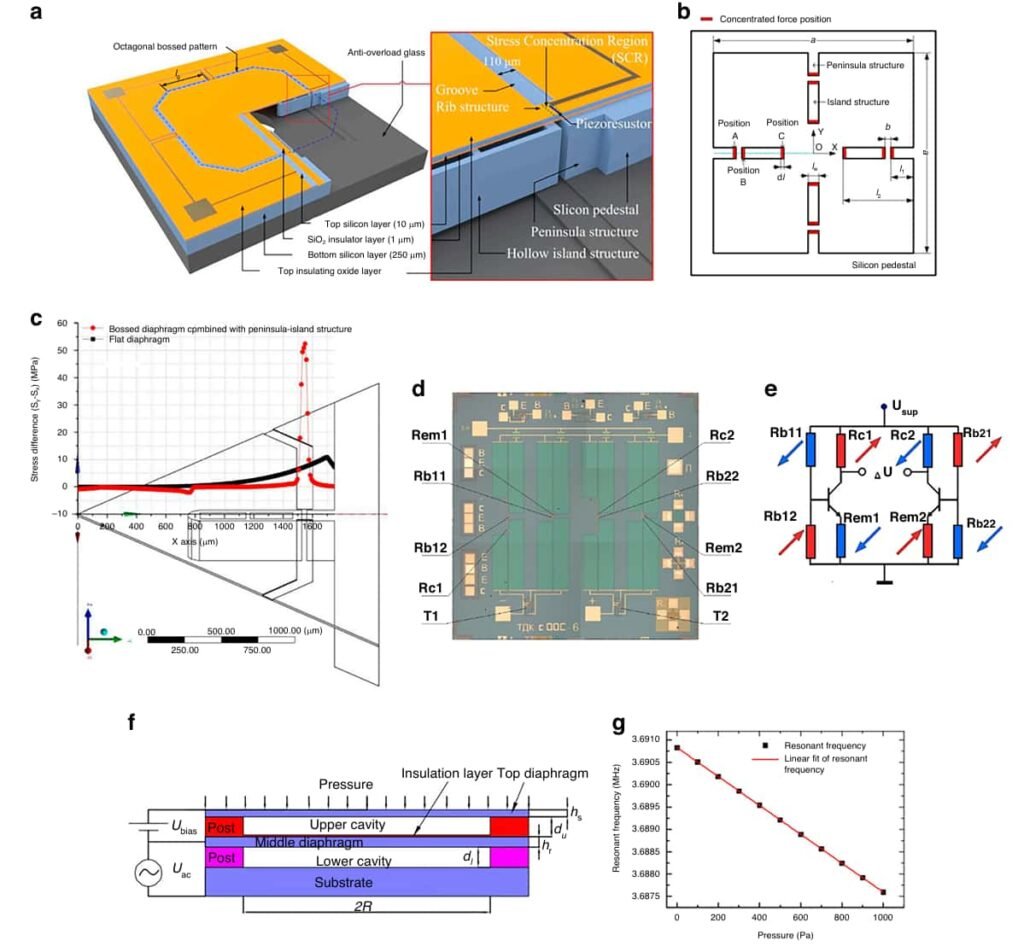
Figure 3 illustrates the critical role of resonant beams in high sensitivity frequency measurements.
Temperature stability can be further improved by utilizing materials such as quartz, while advanced packaging technology ensures long-term reliability.
5.Integrated MEMS Sensor Chip
To meet the need for multifunctional miniaturized devices, researchers have developed chips with integrated pressure, temperature, and vibration sensing, which have important applications in smartphones, automotive systems, and industrial monitoring.
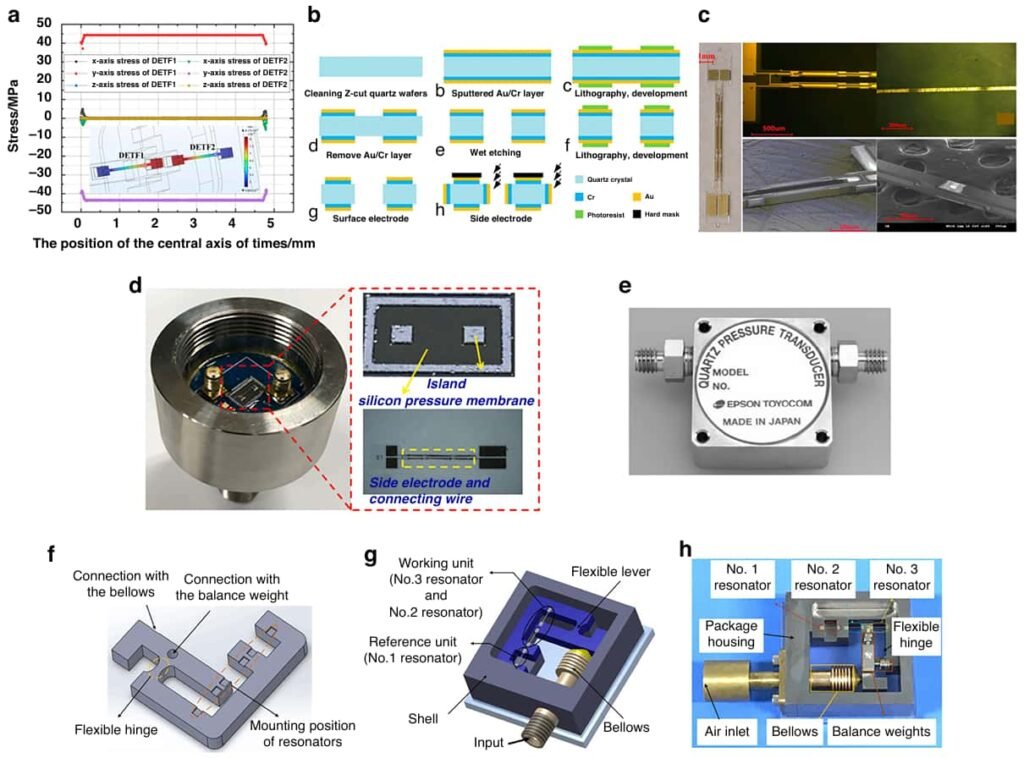
Figure 4 illustrates the integrated chip design, emphasizing its compact form factor and multi-parameter measurement capabilities.
The sensor arrangement is optimized to reduce stress interference, while multilayer bonding technology is used to improve sealing performance and durability.
6.Key challenges and future developments
MEMS pressure sensors still face the challenges of dynamic response capability, temperature compensation, and miniaturization for specific application scenarios. Through the introduction of new materials such as graphene and nanowires, it is expected to further break through the existing technological bottlenecks.
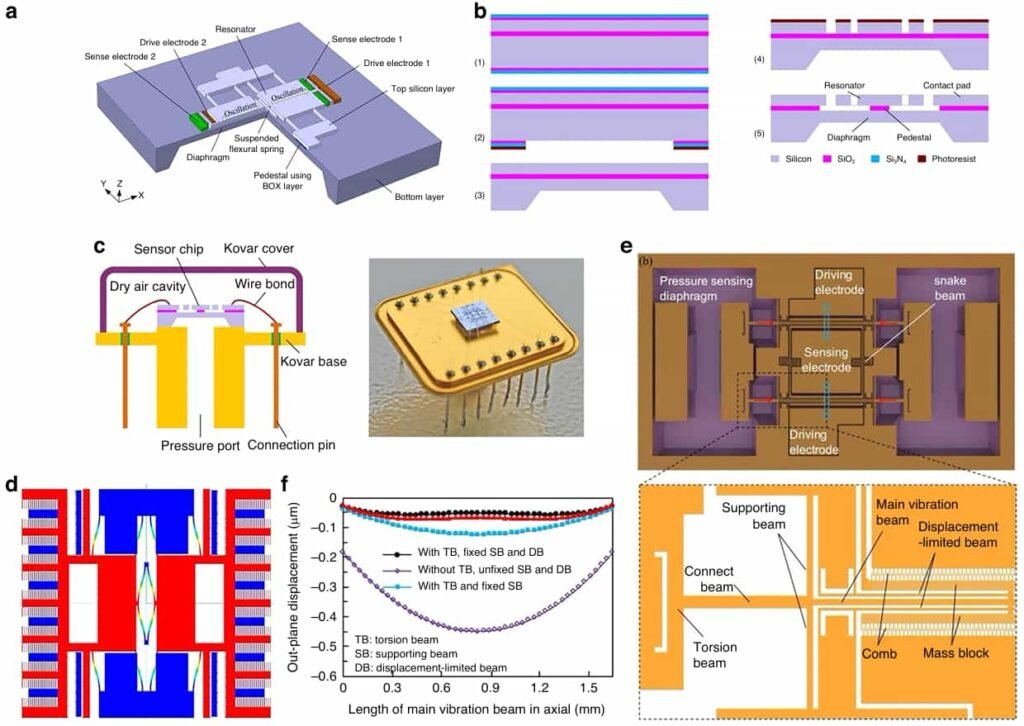
Figure 5 summarizes new advances in materials integration and packaging innovations for MEMS sensors.
Future research should focus on the decoupling of sensitivity and frequency, reduction of nonlinearity, and dynamic performance enhancement to lay the foundation for the application of new generation sensors.
Заклучок
MEMS pressure sensors have become one of the core technologies for multi-industry applications, and their performance has been comprehensively improved through continuous innovations in design, manufacturing and integration technologies. This paper highlights the latest progress of micro differential pressure sensors, resonant pressure sensors and integrated sensing chips. With further optimization of the technology, MEMS sensors will play a more important role in the field of intelligence and high precision.
Горенаведениот вовед само ја гребе површината на апликациите на технологијата на сензорот за притисок. Ќе продолжиме да ги истражуваме различните типови на сензорски елементи што се користат во различни производи, како тие функционираат и нивните предности и недостатоци. Ако сакате повеќе детали за она што се дискутира овде, можете да ја проверите поврзаната содржина подоцна во ова упатство. Ако сте притиснати за време, можете исто така да кликнете овде за да ги преземете деталите за овој водич Податоци за производ на сензорот за притисок на воздухот PDF.
За повеќе информации за други технологии на сензори, ве молиме Посетете ја страницата на нашите сензори.
References
[1] X. Han et al., “Advances in high-performance MEMS pressure sensors: design, fabrication, and packaging,” Microsystems & Nanoengineering, vol. 9, no. 156, pp. 1-34, Dec. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-023-00620-1
Disclaimer: The content of this article is to draw reference to the views of other sites, if there is infringement or other matters, please contact us to delete
