ລາຍການ
Under the backdrop of rapidly growing market demand for electronic control systems in vehicles (as illustrated), automotive sensor technology continues to advance. The overall trends for future automotive sensors include:
ປັນຍາ: Sensors with on-board processing and decision-making capabilities.
miniaturization: Smaller form factors for easier integration and lower cost.
ການປະສົມປະສານ: Combining multiple sensing functions or electronics into a single package.
ການທໍານົ່ມ: One device measuring several physical parameters.
ວັດສະດຸໃຫມ່ & ປະມວນຜົນ: Novel sensor structures enabled by advanced materials and manufacturing techniques.
MEMS-based sensors have become the core components in modern automotive sensing.
ການຈັດປະເພດຂອງເຊັນເຊີລົດຍົນ
Based on system context and function, automotive sensors can be grouped into:
PowerTrain ຄວບຄຸມລະບົບ mems
ລະບົບເຄື່ອງໃຊ້ໄຟຟ້າຂອງຮ່າງກາຍ
ລະບົບຄວາມປອດໄພ Electronics MEMS
ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance System) MEMS
1. Powertrain Control System MEMS
ເຄື່ອງວັດແທກທາງອາກາດ - ການຄວບຄຸມການເຂົ້າຮ່ວມ
ເຄາະທະຫານ - ການຄຸ້ມຄອງເຄື່ອງຈັກ
ເຊັນເຊີ-Height Height - ການຄວບຄຸມການໂຈະ
ເຊັນເຊີແບດເຕີຣີ - ການຄຸ້ມຄອງແບດເຕີລີ່
ເຊັນເຊີອົກຊີເຈນ - ຕິດຕາມກວດກາການປ່ອຍອາຍພິດແລະການຄວບຄຸມ
ເຊັນເຊີຕໍາແຫນ່ງ – start-stop / auto-hold functions
ແຈ & ເຊັນເຊີຕໍາແຫນ່ງ – engine control / steering control
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມກົດດັນ – engine, transmission, turbocharger, and fuel-injection control
2. Body Electronics System MEMS
ເຊັນເຊີແສງສະຫວ່າງ - ການຄວບຄຸມ headlamp ອັດຕະໂນມັດ
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມໄວຂອງປ່ອງຢ້ຽມ - Pinch-Guard ສໍາລັບກໍາລັງໄຟຟ້າ
ຝົນຕົກ - wipers ກະຈົກກະຈົກອັດຕະໂນມັດ
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມກົດດັນ - ລະບົບລັອກສູນກາງ
ເຊັນເຊີຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດ - ການໄດ້ຮັບອາກາດ HVAC
ເຊັນເຊີອຸນຫະພູມ - hvac
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມຊຸ່ມຊື່ນ - hvac
3. Safety Electronics System MEMS
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມກົດດັນສູງ – ESC (Electronic Stability Control)
ເຊັນເຊີມຸມຂອງລໍ້ - ESC
pecelerometer – airbags / ABS
ເຊັນເຊີການພັກເຊົາ - ຖົງລົມນິລະໄພ
Gyro (Yaw-Rate) Sensor - ຖົງລົມນິລະໄພ
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມໄວລໍ້ - ABS
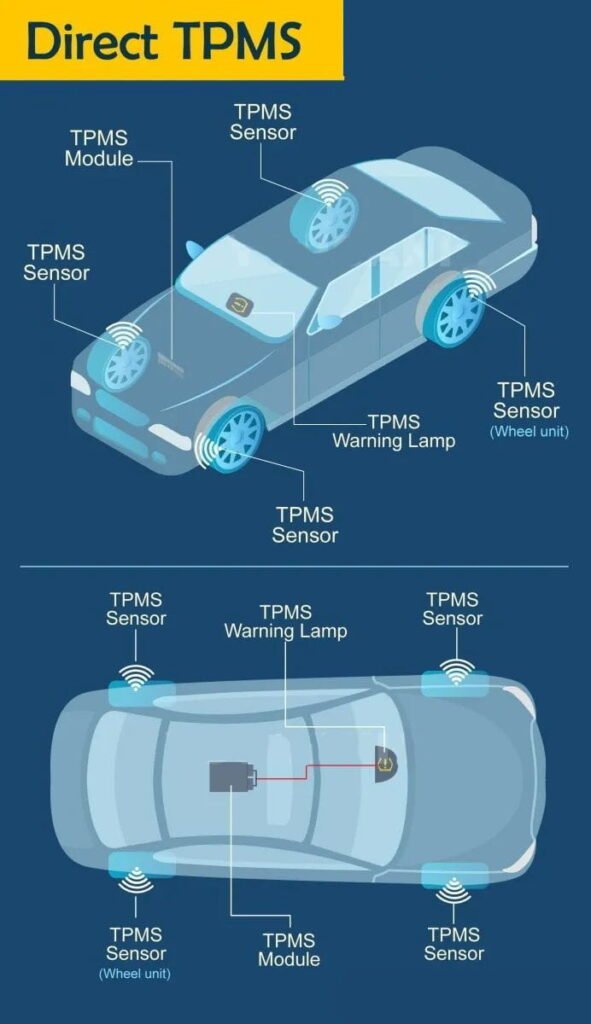
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມກົດດັນ – TPMS (Tire-Pressure Monitoring System)
ເຊັນເຊີອຸນຫະພູມ - TPMS
4. ADAS MEMS
CMOS Image Sensor – lane-keeping / 360° surround view
radar ring millimeter ໄລຍະໄກ – adaptive cruise control / collision warning
lidar – collision warning / autonomous driving
radar-ranimeter-Wave-Wave-Wave - ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອແບບຕາບອດ
ເຊັນມ ultrasonic - ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອບ່ອນຈອດລົດ
ເຊັນເຊີອິນຟາເລດ - ວິໄສທັດໃນຕອນກາງຄືນ
ຄໍາຮ້ອງສະຫມັກຂອງ mems ລົດຍົນ
The automotive market is a major application field for sensors. MEMS automotive sensors serve as critical information sources for vehicle electronic control systems, providing real-time, accurate measurements of temperature, pressure, position, speed, acceleration, vibration, and more. A typical family sedan now carries nearly 100 sensors; luxury vehicles can have up to 200.
Beyond MEMS, the automotive sensor market includes classic active sensors such as odometer sensors, intake/oil pressure sensors, coolant-temperature sensors, air-flow meters, TPMS sensors, chemical sensors, inertial sensors, magnetic sensors, ultrasonic sensors, image sensors, radar, and LiDAR.
ປະເພດ sensor ສໍາຄັນແລະຫນ້າທີ່
Odometer (Mileage) Sensor
ຫຼັກການ: Hall-effect or photoelectric detection.
ຫນ້າທີ່: Calculates vehicle speed and distance using wheel/axle rotational speed (ω) and known tire radius (r):
Distance=r×ω×t.
ການອອກແບບ: Gear-drive style with two bearings on the driveshaft, reducing torque and friction. Connector sits on the transmission housing.
ເຊັນເຊີ-manifold-Manifold
ຫນ້າທີ່: Measures absolute pressure in the intake manifold, outputs voltage to ECU to determine base fuel injection quantity.
ປະເພດທໍາມະດາ: Semiconductor piezoresistive sensors.
ຄໍາຮ້ອງສະຫມັກ: Used on vehicles such as the Audi 100 (V6 engine), Santana 2000, Jeep Cherokee 2.5 L, Toyota Crown 3.0 L, etc.
ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມດັນນ້ໍາມັນ
ຫນ້າທີ່: Monitors engine oil pressure, signals the driver when oil pressure falls below safe levels.
ປະເພດ: Silicon piezoresistive and silicon-capacitive MEMS sensors, integrating sensing element, signal conditioning, and interface electronics.
ເຊັນເຊີອຸນຫະພູມ coolant
ອົງປະກອບພາຍໃນ: Semiconductor thermistor—resistance decreases as temperature rises.
ທີ່ຕັ້ງ: Installed in engine block or cylinder-head water jacket.
ພາລະບົດບາດ: Provides ECU with coolant-temperature data for fuel-injection and ignition timing corrections.
Air-Flow Sensor (MAF)
ຫນ້າທີ່: Converts intake-air mass or volume flow into an electrical signal for the ECU’s fuel-injection calculation.
ປະເພດ:
Vane-type (e.g., Toyota Previa),
Vortex-shedding (e.g., Lexus LS400),
Hot-wire (e.g., Nissan Sunny VG30E),
Hot-film (volumetric and mass-flow models).
ເຊັນເຊີລົດຍົນ
ທີ່ຕັ້ງ: Mounted on brake caliper near the rotor.
ຫຼັກການ: Inductive coil senses a toothed tone ring on the wheel hub; generates a quasi-sine AC signal proportional to wheel speed, sent to the ABS ECU.
Airbag Crash (Impact) Sensor
ປະເພດ:
ແກັບ: Detect rapid deceleration during collision and initiate airbag deployment.
ແກັບທີ່ປອດໄພ: Prevent false deployment in non-collision events.
ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ: Resonant-type and non-resonant accelerometers (piezoelectric or magnetostrictive).
ລະບາຍຄວາມຫມາຍອົກຊີເຈນທີ່ອາຍແກັສ
ຈຸດປະສົງ: Measures O₂ concentration in exhaust to control the air-fuel ratio.
ຕົວປ່ຽນແປງ:
Zirconia ceramic sensor (–40 °C to 900 °C, ±1% accuracy),
Zirconia concentration-cell sensor (300 °C to 800 °C),
Solid-electrolyte oxygen sensor (0 °C to 400 °C, ±0.5% accuracy),
TiO₂ semiconductor sensor (robust against lead contamination).
ຕໍາແຫນ່ງ & ເຊັນເຊີຄວາມໄວ
ຫນ້າທີ່: Monitor crankshaft/camshaft angles, throttle position, vehicle speed, acceleration/deceleration.
ປະເພດ: Alternator-type, magnetoresistive, Hall-effect, reed-switch, optical, and transistor-magnetic sensors.
ເຊັນເຊີເລື່ອນ - ວາງຕໍາແຫນ່ງ: Detects throttle-plate angle via mechanical linkage—switch, variable-resistor, or integrated designs.
ເຊັນເຊີຕໍາແຫນ່ງ crankshaft: Provides top-dead-center, crank angle, and speed signals. Types include inductive, Hall-effect, and optical variants.
ເຄາະທະຫານ: Mounted on engine block to detect knock via vibration—magnetostrictive or piezoelectric.
ຄວາມໄວຂອງຍານພາຫະນະ & Motor RPM Sensors (EV)
ເຊັນເຊີ RPM: Inductive, optical, or Hall-effect, non-contact measurement for safety and precision.
ເຊັນເຊີລົດໄຟ: Electromagnetic, optical, variable-reluctance, or Hall-effect to measure driving speed.
ພາບລວມຂອງຕະຫຼາດ
The automotive sensor segment has become a major application area for MEMS devices. Pressure sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and flow sensors together represent 99% of automotive MEMS applications, with five-year growth rates of 3–12%. MEMS pressure sensors are the most widely used, priced around $5–7 each. In 2018, automotive MEMS pressure-sensor revenue reached $1.8 billion, accounting for 74% of the total MEMS-sensor industry revenue. Key growth drivers include TPMS, ESC brake sensors, side-airbag systems, stricter emissions controls (EGR pressure), and ambient-pressure monitoring.
ໂປແກຼມ Mems ປະຈໍາຕົວລົດໃຫຍ່ຫ້າອັນດັບໂດຍລາຍໄດ້
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ລະບົບແອ
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Tire-Pressure Monitoring (TPMS)
ການຊອກຄົ້ນຫາຂອງ rollover
ການນໍາໃຊ້ mems ທີ່ມີຊື່ສຽງ
High-volume, high-precision, low-cost MEMS are ideal for automotive ECUs.
MEMS accelerometers are replacing legacy electromechanical accelerometers in airbag and ABS systems.
MEMS gyros in high-end vehicles support active suspension and rollover protection.
MEMS pressure sensors embedded in TPMS transmit tire pressure, temperature, and wheel speed wirelessly.
Multi-point MAP sensors improve fuel economy and emissions in EFI systems.
Silicon MEMS pressure sensors are replacing ceramic capacitive sensors in EGR systems.
China, as the world’s largest automotive producer and consumer, has become the largest market for automotive sensor applications. According to IMARC Group, the global automotive-sensor market reached $29.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $72.1 billion by 2033 (CAGR 10.04% from 2025–2033). MEMS technology is steadily displacing traditional sensors as the mainstream for automotive sensing.
China, as the world’s largest automotive producer and consumer, has become the largest market for automotive sensor applications. According to IMARC Group, the global automotive-sensor market reached $29.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $72.1 billion by 2033 (CAGR 10.04% from 2025–2033). MEMS technology is steadily displacing traditional sensors as the mainstream for automotive sensing.
ສະຫຼຸບ
In summary, the rapid expansion of automotive electronic control systems has driven continuous advancement in sensor technologies. Future automotive sensors will be characterized by increased intelligence, miniaturization, integration, multifunctionality, and the adoption of novel materials and processes. MEMS-based sensors are now the backbone of vehicle sensing, spanning powertrain control, body electronics, safety systems, and ADAS. As vehicles become more connected, autonomous, and electrified, the demand for high-performance, reliable, and cost-effective MEMS sensors will only grow. By 2030, global and Chinese automotive sensor markets are poised to see substantial growth, solidifying MEMS technology as the predominant choice for next-generation vehicle sensing applications.
ການແນະນໍາຂ້າງເທິງພຽງແຕ່ scratches ດ້ານຂອງຄໍາຮ້ອງສະຫມັກຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຊີເຊັນເຊີຄວາມກົດດັນ. ພວກເຮົາຈະສືບຕໍ່ຄົ້ນຫາປະເພດຕ່າງໆຂອງອົງປະກອບເຊັນເຊີທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນຜະລິດຕະພັນຕ່າງໆ, ວິທີການເຮັດວຽກ, ແລະຂໍ້ດີແລະຂໍ້ເສຍຂອງມັນ. ຖ້າທ່ານຕ້ອງການລາຍລະອຽດເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບສິ່ງທີ່ໄດ້ສົນທະນາຢູ່ທີ່ນີ້, ທ່ານສາມາດກວດເບິ່ງເນື້ອຫາທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໃນພາຍຫຼັງໃນຄູ່ມືນີ້. ຖ້າຫາກວ່າທ່ານກໍາລັງກົດດັນສໍາລັບການໃຊ້ເວລາ, ທ່ານຍັງສາມາດຄລິກທີ່ນີ້ເພື່ອດາວໂຫລດລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຄູ່ມືນີ້ ຂໍ້ມູນ PDF ຜະລິດຕະພັນ PDOR Air.
ສໍາລັບຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບເຕັກໂນໂລຊີເຊັນເຊີອື່ນໆ, ກະລຸນາ ເຂົ້າເບິ່ງຫນ້າສັນຍາລັກຂອງພວກເຮົາ.

I blog frequently and I seriously thank you for your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest. I will take a note of your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.