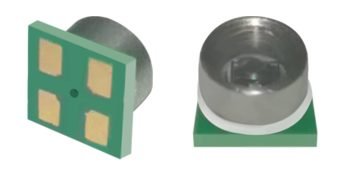
As blood pressure monitors are becoming more and more important devices in the health monitoring field, the choice of core sensors directly affects product performance and user experience. In the design and manufacturing process, deciding whether to use analog or digital sensors becomes a critical decision.
In sports, the human body’s heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygen, etc. are several important features, and the collection and processing of these data can help analyze the exercise behavior to improve the exercise mode and achieve better exercise results. Among them, blood oxygen, heart rate through the optical way, in the wearable device has been a better solution, such as electronic bracelets, watches, are now equipped with led optical module, for heart rate and blood oxygen monitoring. Human blood pressure is an important reference for athletes to analyze their physical fitness. For blood pressure measurement on wearable devices, compact, miniature, and wearable products are still relatively blank in the market, WF, as a MEMS technology platform enterprise, has launched two types of sensors, digital and analog versions, which provide benchmark solutions for human blood pressure measurement on wearable devices.
In this article, we will discuss the characteristics, application scenarios and applicability of the two sensors to help developers choose the best solution.

읽기를 시작해 볼까요!
목차
Analog Sensors: The Flexible Choice of Tradition
Characteristic analysis
The output signal of an analog sensor is a continuous voltage or current value directly proportional to the pressure change. This design provides good flexibility, but also brings some design challenges:
1. High signal processing requirements: Since analog signals are sensitive to noise, external circuits need to include signal amplification, filtering, and other functions to improve signal accuracy.
2. Reliance on ADC modules: In order to convert analog signals into processable digital signals, an additional analog-to-digital converter (ADC) must be integrated into the system.
3. Low-cost advantage: Analog sensors are usually low-cost to manufacture and are suitable for cost-sensitive devices.
응용 프로그램 시나리오
- Entry-level sphygmomanometer watches: Analog sensors are an economical choice for watches with relatively simple functions and moderate accuracy requirements.
- Flexible design: Development teams can optimize sensitivity and range to meet specific needs by adjusting peripheral circuit parameters.
Digital Sensors: High-Performance Intelligent Solutions
Feature Analysis
디지털 센서 have an advantage in signal output. The built-in analog-to-digital converter module and signal processing unit can directly convert sensor data into digital signals such as I2C, SPI or UART for transmission, with the following features:
1. Simple development: no need for complex peripheral circuit design, greatly reducing the difficulty of hardware design and development.
2. Strong anti-interference ability: digital signals are not sensitive to external electromagnetic interference, ensuring the accuracy and stability of data transmission.
3. High accuracy and stability: Many digital sensors have built-in temperature compensation to provide reliable measurement results in different environments.
Applicable Scenarios
- High-end smart sphygmomanometer watches: Digital sensors are a better choice for devices that require higher accuracy, stability, and user experience.
- Fast time-to-market: The plug-and-play nature of digital sensors helps to shorten the development cycle and accelerate product introduction into the market.
Analog vs Digital Sensors: Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages
The following is a summary of the comparison between the two sensors to help developers quickly evaluate their advantages and disadvantages:
| 특징 | 아날로그 센서 | 디지털 센서 |
|---|---|---|
| Output signals | Analog voltage/current | Digital signals (I2C/SPI, etc.) |
| Development complexity | High (peripheral circuit design required) | Low (built-in signal processing) |
| Interference immunity | Weak | Strong |
| Accuracy and stability | Dependent on external circuit optimization | Built-in compensation for high stability |
| 비용 | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Interface Type | ADC Requirements | I2C/SPI |
Application Advice: How to choose the right sensor?
Economical Blood Pressure Monitors
Analog sensors are a good choice if the product target market is focused on price/performance ratio and the development team has strong signal processing capabilities. These sensors can fulfill basic blood pressure measurement needs while keeping costs under control.
High-end Intelligent Blood Pressure Monitor
If the product is positioned at the high end of the market and the user’s needs are centered on high accuracy, stability, and fast response time, then digital sensors are definitely more suitable. The built-in intelligence reduces development difficulties and improves overall performance.
결론
Finding the Balance to Define the Best Applications for Sensors
Analog and digital sensors each have distinct advantages and applications. Analog sensors are suitable for entry-level products due to their low cost and flexibility, while digital sensors are preferred for high-end devices due to their high performance and ease of use. The final choice should be based on the device’s design goals, performance requirements and budget.
By making the right sensor choice, you can ensure that your blood pressure monitor strikes the optimal balance between functionality and user experience, allowing users to benefit more from their daily health monitoring.