カタログ
High-resolution MEMS pressure sensors, when integrated into pneumatic caulking equipment, provide real-time pressure monitoring and closed-loop control. That stability keeps dispense volume steady, cuts material waste, and raises equipment reliability. Based on collected images and technical notes, this article explains sensor basics, precise dispense control, protection and safety features, automation integration, and energy and maintenance gains
1. MEMS Pressure Sensor Basics and How They Work
センシングメカニズムと信号の流れ
MEMS piezoresistive sensors use a silicon diaphragm that flexes under pressure. That flex changes embedded resistor values in a Wheatstone bridge. The bridge output is amplified and conditioned, then delivered as analog or digital output. Typical response is 1–5 ms and resolution can reach 0.05% FS. Interfaces commonly include I²C, SPI, and 4–20 mA, which plug directly into PLCs or MCUs for closed-loop control.
パッケージングと電気特性
Modern packages are compact, often ceramic or metal, with pins for power, ground, signal, and calibration. Many include a temperature sensor for onboard compensation. Typical supply voltages are 3.3 V or 5 V and power draw is low—suitable for handheld or line equipment. Mount sensors near the regulator or nozzle to reduce dead volume and speed response.

2. Precise Control of Sealant Output
リアルタイム圧力フィードバックと閉ループ制御
Pressure sensors stream pressure curves to the controller. The controller adjusts pump power or valve position to hold setpoint pressure, keeping extrusion steady. This closed-loop removes effects of source fluctuations, line resistance, and temperature shifts. Target control accuracy of ±0.5% FS is realistic with a properly tuned loop, improving bead width and flow repeatability.
材料適応圧力調整
Different sealants need different drive pressures. The control system uses pressure rise, steady-state pressure, and optionally temperature to select the correct control profile. High-viscosity materials run at higher steady pressure; low-viscosity materials need lower pressure to avoid over-dispense. Automating profile call-up reduces manual setup and speeds changeovers.
温度補償と環境処理
Temperature affects sealant rheology and air properties. Built-in temperature compensation or a simple pressure–temperature matrix helps correct measurement drift and maintain consistent flow. Proper compensation keeps performance stable across a wide working range (roughly −20°C to +60°C in typical designs).
3. Equipment Protection and Safety Monitoring
過剰圧力保護と緊急シャットダウン
Sensors trigger protection when pressure exceeds safe limits—common causes include nozzle clog, kinked hose, or cured material blocking flow. Set safety thresholds and a fast response path to stop pumps or close valves. Response times under 10 ms and clear fault logging protect equipment and operators from spray or mechanical failure.
低圧アラートと供給チェック
Low pressure indicates source issues or leaks and can ruin a run. Low-pressure alarms notify operators before quality suffers. Set low-pressure thresholds to avoid false alarms while still catching real faults. Monitoring pressure rise time gives a quick view of system sealing health.
4. Automation and Intelligent Integration
PLC統合とラインレベルの制御
MEMS sensors talk to PLCs over standard buses, providing live pressure and status. PLCs load product-specific pressure programs so the line can switch products with minimal delay. Multi-station coordination keeps bead quality consistent across work stations and simplifies production flow.
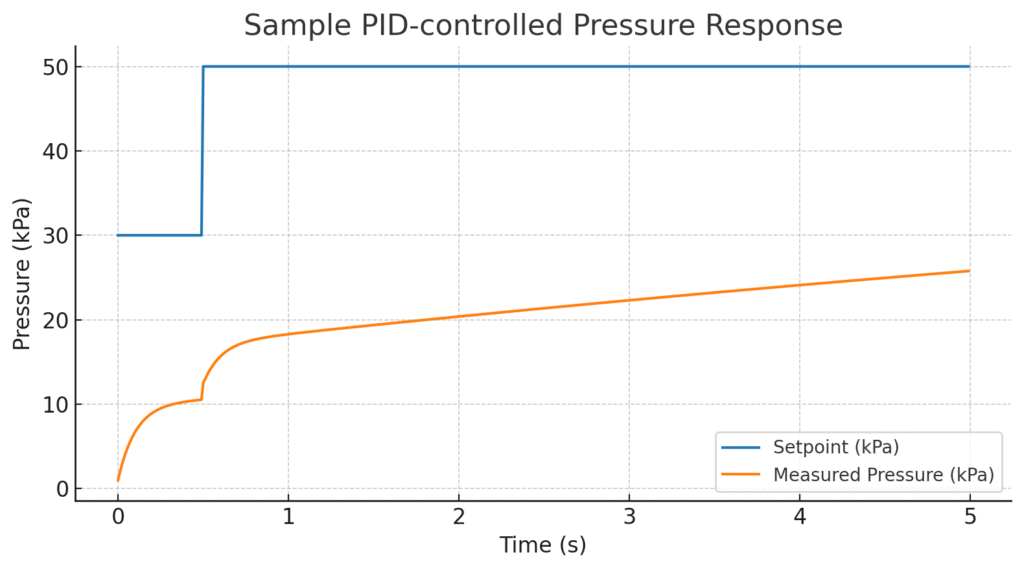
データのキャプチャとプロセスチューニング
Store pressure trends, alarms, and event markers for offline analysis. Trend data helps spot nozzle wear, pump degradation, or material change. Use logged data to tune control parameters or build simple predictive models for maintenance planning. Aggregated data improves repeatability and reduces downtime.
5. Energy Efficiency and Equipment Life
オンデマンドの圧力とエネルギー節約
Instead of constant high-pressure supply, use demand-driven control: lower pressure in standby, ramp up only when dispensing. For intermittent work this can cut compressor runtime and energy use substantially—typical savings in the 20–30% range in many setups.
摩耗削減とメンテナンスのスケジューリング
Stable pressure reduces shock loading on seals, valves, and fittings. Track pressure fluctuation patterns to identify components that are degrading. Condition-based maintenance guided by sensor data is more efficient than fixed-interval servicing and can extend component life by double-digit percentages.
結論
Using high-performance MEMS pressure sensors as the feedback core of pneumatic caulking equipment converts manual guesswork into repeatable, controllable process parameters. Real-time monitoring, closed-loop control, safety cutoffs, material-adaptive profiles, and data-driven maintenance together raise dispense consistency, safety, and energy efficiency. With correct mounting, sampling, filtering, alarm thresholds, and PID tuning, teams can deploy stable, production-grade caulking systems that scale from single tools to automated lines.
上記の紹介は、圧力センサー技術のアプリケーションの表面をなぞっただけです。私たちは、さまざまな製品で使用されているさまざまなタイプのセンサー素子、それらがどのように機能するか、そしてそれらの長所と短所を引き続き調査していきます。ここで説明する内容についてさらに詳しく知りたい場合は、このガイドの後半にある関連コンテンツをご覧ください。時間がない場合は、ここをクリックしてこのガイドの詳細をダウンロードすることもできます。 空気圧センサー製品PDFデータ。
他のセンサー技術の詳細については、こちらをご覧ください。 センサーページにアクセスしてください。
