Systèmes microélectromécaniques (Mems) Les capteurs de pression sont largement utilisés dans une variété d'industries, y compris l'automobile, aérospatial et médical, et sont devenus des appareils importants pour l'ingénierie moderne en raison de leur grande précision et de leur petite taille. Au cours des dernières années, Les capteurs de pression ont fait des progrès importants dans la conception, technologies de fabrication et d'emballage, Et leurs performances ont été considérablement améliorées. Dans ce document, Nous discuterons des dernières tendances des micro-capteurs de pression différentielle (MDPS), capteurs de pression résonnante (RPS), puces de détection intégrées, et capteurs de pression miniaturisés.

Catalogue
Laisser’s commence à comprendre!
1.Principes de base des capteurs de pression MEMS
Les capteurs de pression MEMS fonctionnent à base de piézorésistance, capacitif, principes piézoélectriques ou résonnants. Par exemple, Les capteurs piézorésives mesurent la pression à travers un pont de Wheatstone et ont une sensibilité élevée. Cependant, Des facteurs tels que la dérive à haute température affectent leur précision, qui est devenu un défi limitant leur développement. Les capteurs capacitifs sont caractérisés par une faible consommation d'énergie et une bonne stabilité de la température, Mais les effets parasites ont un impact sur leur précision.
2. Micro-capteur de pression différentielle (MDPS)
MDPS est largement utilisé dans l'équipement médical, Surveillance de la pression de la prise d'incendie, etc.. Il convient particulièrement aux mesures de haute précision dans les plages de petites pression. Au cours des dernières années, Les MDP sont passés de la structure de la membrane plate traditionnelle à une conception plus complexe de «l'île-Membrane» pour améliorer la sensibilité et réduire la non-linéarité.
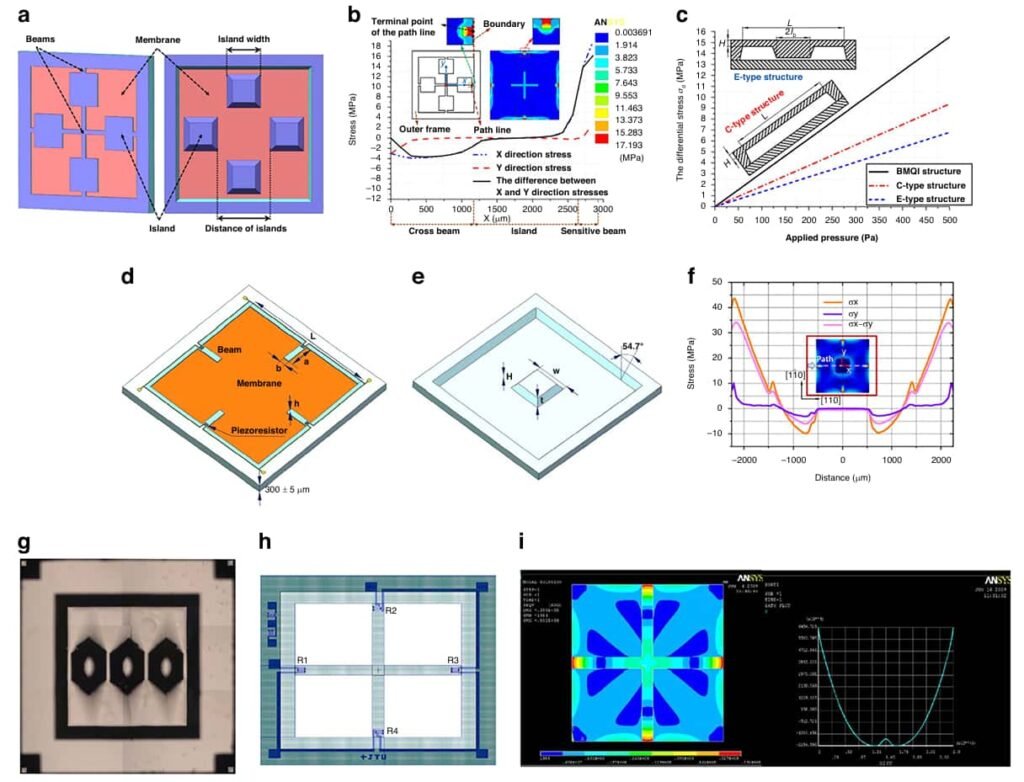
Chiffre 1 illustre l'évolution de la conception du MDPS d'une membrane plate à une île de membrane de faisceau, avec une augmentation significative de la sensibilité et une concentration de contraintes plus optimisée.
Cette structure atteint une sensibilité de 11.098 μV / v / pa dans la gamme de 0-500 Pennsylvanie, qui est une amélioration significative par rapport aux structures de type C et à la membrane plate. Les optimisations ultérieures incluent une conception de faisceau croisé et une structure île creuse pour améliorer encore la distribution des contraintes et les performances dynamiques.
3. Technologie de fabrication MDPS
La fabrication MDPS nécessite des processus de gravure de haute précision, y compris la gravure des ions réactifs profonds (TROIS) et les processus de dopage de bore, pour former les piézorésistants. La gravure de la couche d'arrêt est essentielle pour contrôler l'épaisseur du diaphragme et aide à maintenir une sensibilité élevée.
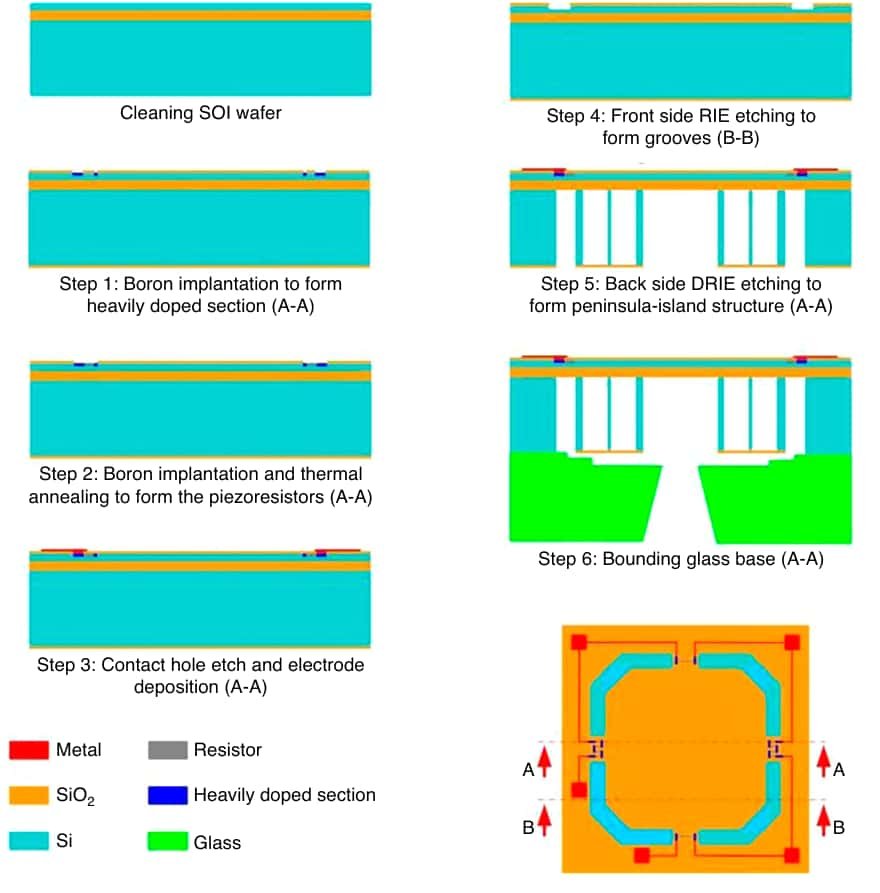
- Chiffre 2 illustre les étapes clés de la fabrication de MDP, souligner l'importance de la précision de la gravure pour l'uniformité du film.
- L'intégration des circuits d'amplification du signal améliore encore la sensibilité, avec quelques créations atteignant 44.9 MV / V / KPA.
4.Capteurs de pression résonnante (RPS)
Les capteurs de pression de résonance sont largement utilisés dans des champs haut de gamme tels que la surveillance aérospatiale et météorologique en raison de leur grande précision et stabilité. Ces capteurs réalisent la mesure de la pression en mesurant les caractéristiques de la variation de fréquence de faisceau de résonance avec la pression.
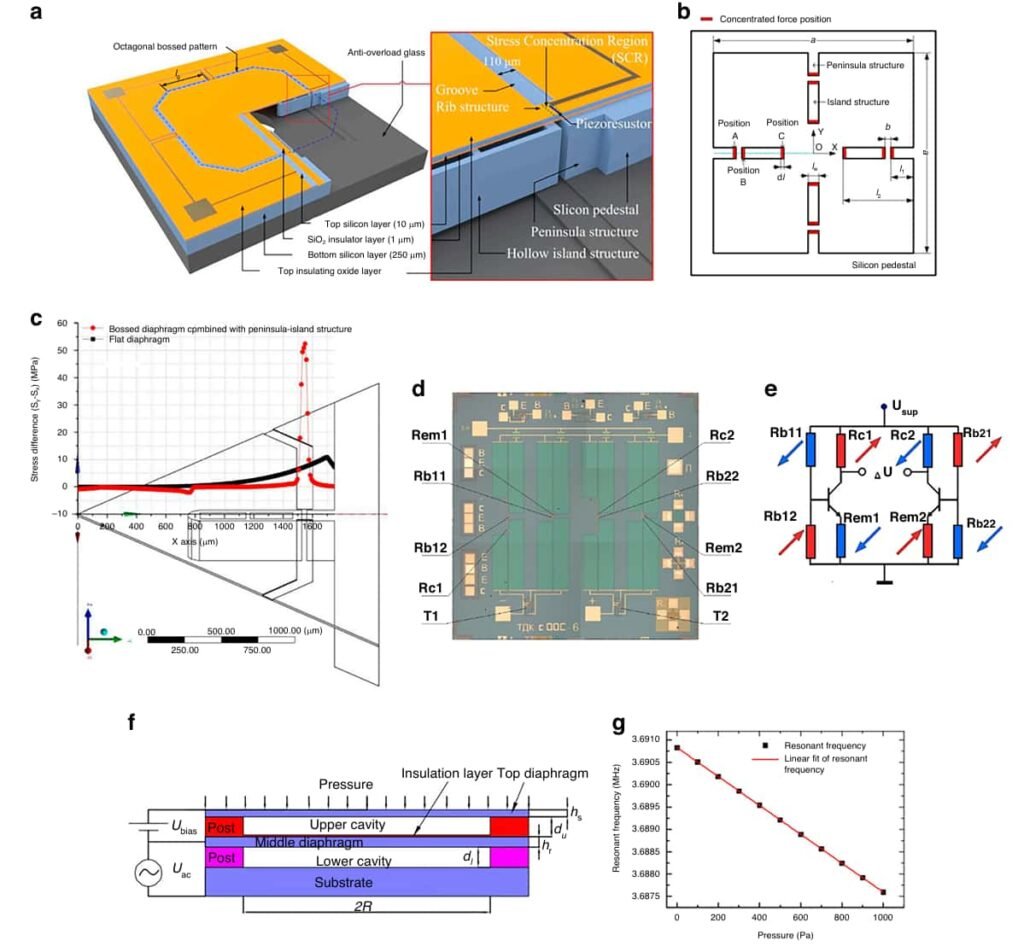
Chiffre 3 illustre le rôle critique des faisceaux de résonance dans les mesures de fréquence à haute sensibilité.
La stabilité de la température peut être encore améliorée en utilisant des matériaux tels que le quartz, tandis que la technologie d'emballage avancée assure une fiabilité à long terme.
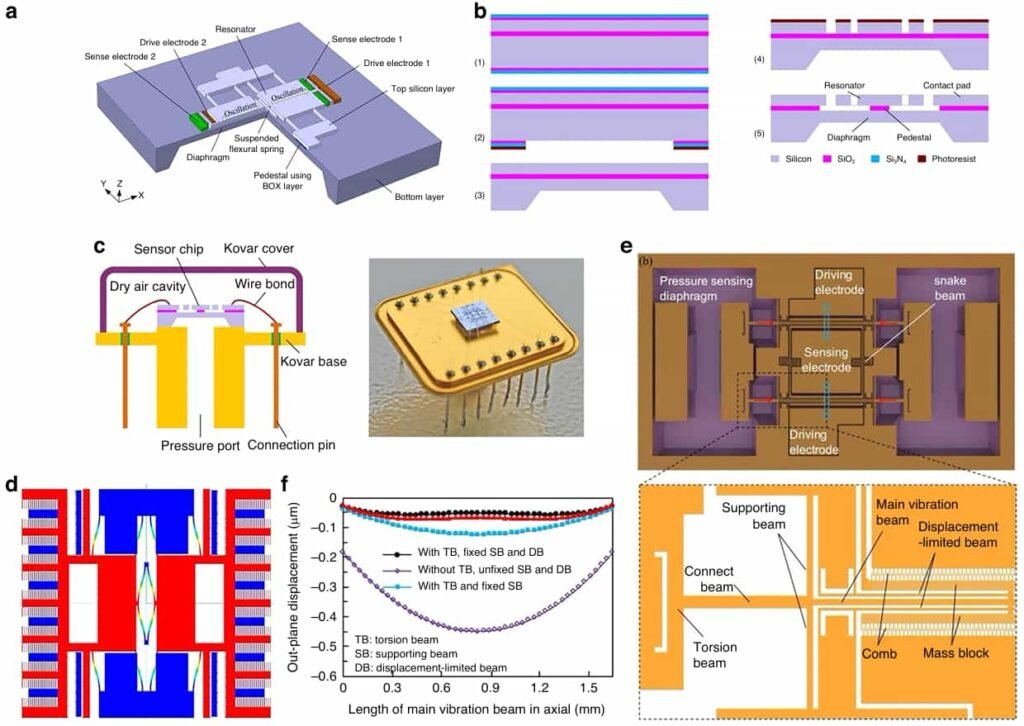
5.Puce de capteur MEMS intégré
Pour répondre au besoin d'appareils miniaturisés multifonctionnels, Les chercheurs ont développé des puces à pression intégrée, température, et détection des vibrations, qui ont des applications importantes dans les smartphones, systèmes automobiles, et surveillance industrielle.
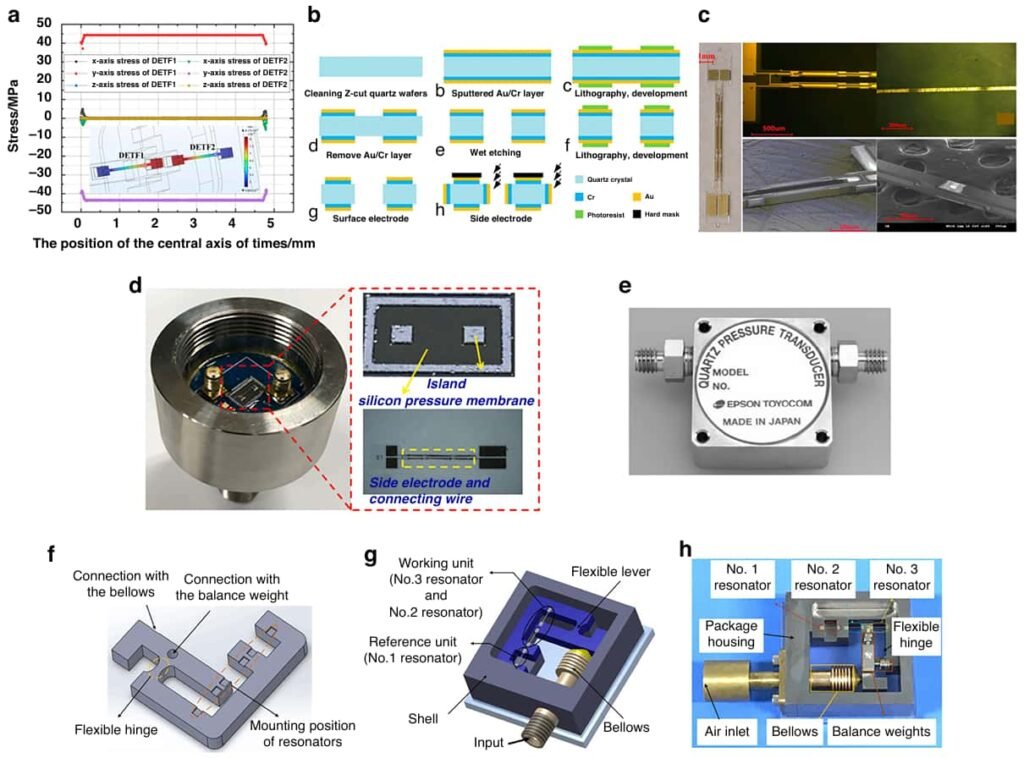
Chiffre 4 illustre la conception de puces intégrée, souligner son facteur de forme compact et ses capacités de mesure multi-paramètres.
La disposition du capteur est optimisée pour réduire les interférences de contrainte, tandis que la technologie de liaison multicouche est utilisée pour améliorer les performances et la durabilité de l'étanchéité.
6.Défis clés et développements futurs
Les capteurs de pression MEMS sont toujours confrontés aux défis de la capacité de réponse dynamique, compensation de température, et miniaturisation pour des scénarios d'application spécifiques. Grâce à l'introduction de nouveaux matériaux tels que le graphène et les nanofils, Il devrait percer davantage les goulots d'étranglement technologiques existants.
Chiffre 5 Résume les nouvelles avancées dans l'intégration des matériaux et les innovations d'emballage pour les capteurs MEMS.
Les recherches futures devraient se concentrer sur le découplage de la sensibilité et de la fréquence, réduction de la non-linéarité, et amélioration des performances dynamiques pour jeter les bases de l'application de capteurs de nouvelle génération.
Conclusion
Les capteurs de pression MEMS sont devenus l'une des technologies de base pour les applications multi-industries, Et leurs performances ont été complètement améliorées grâce à des innovations continues dans la conception, technologies de fabrication et d'intégration. Cet article met en évidence les dernières progrès des micro-capteurs de pression différentielle, capteurs de pression résonnante et puces de détection intégrées. Avec une optimisation supplémentaire de la technologie, Les capteurs MEMS joueront un rôle plus important dans le domaine de l'intelligence et de la haute précision.
L'introduction ci-dessus ne fait que gratter la surface des applications de la technologie du capteur de pression. Nous continuerons d'explorer les différents types d'éléments de capteur utilisés dans divers produits, Comment ils fonctionnent, et leurs avantages et leurs inconvénients. Si tu’D Like plus de détails sur ce’S discuté ici, Vous pouvez consulter le contenu connexe plus tard dans ce guide. Si vous êtes pressé par le temps, Vous pouvez également cliquer ici pour télécharger les détails de ces guides Données PDF du produit du capteur de pression d'air.
Pour plus d'informations sur d'autres technologies de capteurs, s'il te plaît Visitez notre page de capteurs.
Références
[1] X. Ils ont et al., « Progrès des capteurs de pression MEMS à haute performance: conception, fabrication, et emballage, » Microsystèmes & Nano-ingénierie, vol. 9, Non. 156, pp. 1-34, Déc. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/S41378-023-00620-1
Clause de non-responsabilité: Le contenu de cet article est de référence aux vues d'autres sites, S'il y a une contrefaçon ou d'autres questions, Veuillez nous contacter pour supprimer


