Catalogar
Under the backdrop of rapidly growing market demand for electronic control systems in vehicles (as illustrated), automotive sensor technology continues to advance. The overall trends for future automotive sensors include:
Inteligencia: Sensors with on-board processing and decision-making capabilities.
Miniaturización: Smaller form factors for easier integration and lower cost.
Integración: Combining multiple sensing functions or electronics into a single package.
Multifuncionalidad: One device measuring several physical parameters.
Nuevos materiales & Procesos: Novel sensor structures enabled by advanced materials and manufacturing techniques.
MEMS-based sensors have become the core components in modern automotive sensing.
Clasificación de sensores automotrices
Based on system context and function, automotive sensors can be grouped into:
MEMS del sistema de control del tren motriz
MEMS del sistema electrónica del cuerpo
MEMS del sistema electrónica de seguridad
ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance System) MEMS
1. Powertrain Control System MEMS
Medidor de flujo de masa de aire - Control de admisión
Sensor de golpe - Gestión del motor
Sensor de algodón de paseo - Control de suspensión
Sensor de batería inteligente - Administración de baterías
Sensor de oxígeno - Monitoreo y control de emisiones de escape
Sensor de posición de pedal – start-stop / auto-hold functions
Ángulo & Sensores de posición – engine control / steering control
Sensores de presión – engine, transmission, turbocharger, and fuel-injection control
2. Body Electronics System MEMS
Sensor de luz ambiental - Control automático de faros
Sensor de velocidad de elevación de la ventana -Guente de pellizco para ventanas eléctricas
Sensor de lluvia - Limpiantadores automáticos del parabrisas
Sensores de presión - Sistema de bloqueo central
Sensor de calidad del aire - Engumeta de aire HVAC
Sensor de temperatura - HVAC
Sensor de humedad - HVAC
3. Safety Electronics System MEMS
Sensor de alta presión – ESC (Electronic Stability Control)
Sensor de ángulo de la rueda de dirección - ESC
Acelerómetro – airbags / ABS
Sensor de ocupación de asiento - Airbags
Gyro (Yaw-Rate) Sensor - Airbags
Sensor de velocidad de la rueda - ABS
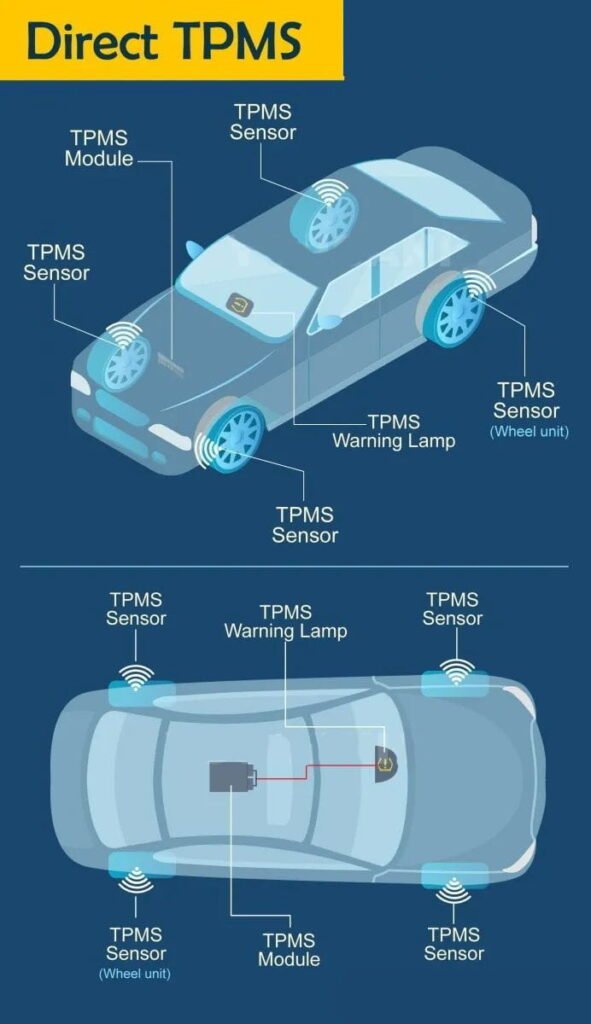
Sensor de presión – TPMS (Tire-Pressure Monitoring System)
Sensor de temperatura - TPMS
4. ADAS MEMS
Sensor de imagen CMOS – lane-keeping / 360° surround view
Radar de onda milímetro de largo alcance – adaptive cruise control / collision warning
Lidar – collision warning / autonomous driving
Radar de onda milímetro -Asistencia de punto ciego
Sensor ultrasónico - Ayuda de estacionamiento
Sensor infrarrojo - Visión nocturna
Aplicaciones de MEMS automotrices
The automotive market is a major application field for sensors. MEMS automotive sensors serve as critical information sources for vehicle electronic control systems, providing real-time, accurate measurements of temperature, pressure, position, speed, acceleration, vibration, and more. A typical family sedan now carries nearly 100 sensors; luxury vehicles can have up to 200.
Beyond MEMS, the automotive sensor market includes classic active sensors such as odometer sensors, intake/oil pressure sensors, coolant-temperature sensors, air-flow meters, TPMS sensors, chemical sensors, inertial sensors, magnetic sensors, ultrasonic sensors, image sensors, radar, and LiDAR.
Tipos de sensores clave y funciones
Odometer (Mileage) Sensor
Principio: Hall-effect or photoelectric detection.
Función: Calculates vehicle speed and distance using wheel/axle rotational speed (ω) and known tire radius (r):
Distance=r×ω×t.
Diseño: Gear-drive style with two bearings on the driveshaft, reducing torque and friction. Connector sits on the transmission housing.
Sensor de presión de admisión
Función: Measures absolute pressure in the intake manifold, outputs voltage to ECU to determine base fuel injection quantity.
Tipos comunes: Semiconductor piezoresistive sensors.
Aplicaciones: Used on vehicles such as the Audi 100 (V6 engine), Santana 2000, Jeep Cherokee 2.5 L, Toyota Crown 3.0 L, etc.
Sensor de presión de aceite
Función: Monitors engine oil pressure, signals the driver when oil pressure falls below safe levels.
Tipos: Silicon piezoresistive and silicon-capacitive MEMS sensors, integrating sensing element, signal conditioning, and interface electronics.
Sensor de temperatura de refrigerante
Elemento interno: Semiconductor thermistor—resistance decreases as temperature rises.
Ubicación: Installed in engine block or cylinder-head water jacket.
Role: Provides ECU with coolant-temperature data for fuel-injection and ignition timing corrections.
Air-Flow Sensor (MAF)
Función: Converts intake-air mass or volume flow into an electrical signal for the ECU’s fuel-injection calculation.
Tipos:
Vane-type (e.g., Toyota Previa),
Vortex-shedding (e.g., Lexus LS400),
Hot-wire (e.g., Nissan Sunny VG30E),
Hot-film (volumetric and mass-flow models).
Sensor de velocidad de la rueda de ABS
Ubicación: Mounted on brake caliper near the rotor.
Principio: Inductive coil senses a toothed tone ring on the wheel hub; generates a quasi-sine AC signal proportional to wheel speed, sent to the ABS ECU.
Airbag Crash (Impact) Sensor
Tipos:
Sensores de activación: Detect rapid deceleration during collision and initiate airbag deployment.
Sensores de seguridad: Prevent false deployment in non-collision events.
Tecnologías: Resonant-type and non-resonant accelerometers (piezoelectric or magnetostrictive).
Sensor de oxígeno de gas de escape
Objetivo: Measures O₂ concentration in exhaust to control the air-fuel ratio.
Variantes:
Zirconia ceramic sensor (–40 °C to 900 °C, ±1% accuracy),
Zirconia concentration-cell sensor (300 °C to 800 °C),
Solid-electrolyte oxygen sensor (0 °C to 400 °C, ±0.5% accuracy),
TiO₂ semiconductor sensor (robust against lead contamination).
Posición & Sensores de velocidad
Funciones: Monitor crankshaft/camshaft angles, throttle position, vehicle speed, acceleration/deceleration.
Tipos: Alternator-type, magnetoresistive, Hall-effect, reed-switch, optical, and transistor-magnetic sensors.
Sensor de posposición del acelerador: Detects throttle-plate angle via mechanical linkage—switch, variable-resistor, or integrated designs.
Sensor de posición del cigüeñal: Provides top-dead-center, crank angle, and speed signals. Types include inductive, Hall-effect, and optical variants.
Sensor de golpe: Mounted on engine block to detect knock via vibration—magnetostrictive or piezoelectric.
Velocidad del vehículo & Motor RPM Sensors (EV)
Sensor de rpm motor: Inductive, optical, or Hall-effect, non-contact measurement for safety and precision.
Sensor de velocidad del vehículo: Electromagnetic, optical, variable-reluctance, or Hall-effect to measure driving speed.
Descripción general del mercado
The automotive sensor segment has become a major application area for MEMS devices. Pressure sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and flow sensors together represent 99% of automotive MEMS applications, with five-year growth rates of 3–12%. MEMS pressure sensors are the most widely used, priced around $5–7 each. In 2018, automotive MEMS pressure-sensor revenue reached $1.8 billion, accounting for 74% of the total MEMS-sensor industry revenue. Key growth drivers include TPMS, ESC brake sensors, side-airbag systems, stricter emissions controls (EGR pressure), and ambient-pressure monitoring.
Las cinco mejores aplicaciones de MEMS automotriz por ingresos
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Sistemas de airbag
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Tire-Pressure Monitoring (TPMS)
Detección
Aplicaciones de MEMS notables
High-volume, high-precision, low-cost MEMS are ideal for automotive ECUs.
MEMS accelerometers are replacing legacy electromechanical accelerometers in airbag and ABS systems.
MEMS gyros in high-end vehicles support active suspension and rollover protection.
MEMS pressure sensors embedded in TPMS transmit tire pressure, temperature, and wheel speed wirelessly.
Multi-point MAP sensors improve fuel economy and emissions in EFI systems.
Silicon MEMS pressure sensors are replacing ceramic capacitive sensors in EGR systems.
China, as the world’s largest automotive producer and consumer, has become the largest market for automotive sensor applications. According to IMARC Group, the global automotive-sensor market reached $29.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $72.1 billion by 2033 (CAGR 10.04% from 2025–2033). MEMS technology is steadily displacing traditional sensors as the mainstream for automotive sensing.
China, as the world’s largest automotive producer and consumer, has become the largest market for automotive sensor applications. According to IMARC Group, the global automotive-sensor market reached $29.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $72.1 billion by 2033 (CAGR 10.04% from 2025–2033). MEMS technology is steadily displacing traditional sensors as the mainstream for automotive sensing.
Conclusión
In summary, the rapid expansion of automotive electronic control systems has driven continuous advancement in sensor technologies. Future automotive sensors will be characterized by increased intelligence, miniaturization, integration, multifunctionality, and the adoption of novel materials and processes. MEMS-based sensors are now the backbone of vehicle sensing, spanning powertrain control, body electronics, safety systems, and ADAS. As vehicles become more connected, autonomous, and electrified, the demand for high-performance, reliable, and cost-effective MEMS sensors will only grow. By 2030, global and Chinese automotive sensor markets are poised to see substantial growth, solidifying MEMS technology as the predominant choice for next-generation vehicle sensing applications.
La introducción anterior sólo toca la superficie de las aplicaciones de la tecnología de sensores de presión. Continuaremos explorando los diferentes tipos de elementos sensores utilizados en diversos productos, cómo funcionan y sus ventajas y desventajas. Si desea obtener más detalles sobre lo que se analiza aquí, puede consultar el contenido relacionado más adelante en esta guía. Si tiene poco tiempo, también puede hacer clic aquí para descargar los detalles de estas guías. Producto del sensor de presión de aire datos PDF.
Para obtener más información sobre otras tecnologías de sensores, por favor Visite nuestra página de sensores.

I blog frequently and I seriously thank you for your information. This great article has truly peaked my interest. I will take a note of your blog and keep checking for new information about once per week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.